Brain herniation
Herniation syndrome; Transtentorial herniation; Uncal herniation; Subfalcine herniation; Tonsillar herniation; Herniation - brainBrain herniation is the shifting of the brain tissue from one space in the skull to another through various folds and openings.
Causes
Brain herniation occurs when something inside the skull produces pressure that moves brain tissues. This is most often the result of brain swelling or bleeding from a head injury, stroke, or brain tumor.
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...

Brain herniation can be a side effect of tumors in the brain, including:
-
Metastatic brain tumor
Metastatic brain tumor
A metastatic brain tumor is cancer that started in another part of the body and has spread to the brain.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Primary brain tumor
Primary brain tumor
A primary brain tumor is a group (mass) of abnormal cells that start in the brain.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Herniation of the brain can also be caused by other factors that lead to increased pressure inside the skull, including:
- Collection of pus and other material in the brain, usually from a bacterial or fungal infection (abscess)
Abscess
A brain abscess is a collection of pus, immune cells, and other material in the brain, caused by a bacterial or fungal infection.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bleeding in the brain (hemorrhage)
- Buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to brain swelling (hydrocephalus)
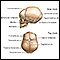
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to the brain pushing against the skull. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Strokes that cause brain swelling
- Swelling after radiation therapy
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-powered radiation (such as x-rays or gamma rays), particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Defect in brain structure, such as a condition called Arnold-Chiari malformation
- Swelling due to loss of oxygen (hypoxia) to the brain
Hypoxia
Cerebral hypoxia occurs when there is not enough oxygen getting to the brain. The brain needs a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients to function....
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Brain herniation can occur:
- From side to side or down, under, or across rigid membrane like the tentorium or falx
- Through a natural bony opening at the base of the skull called the foramen magnum
- Through openings created during brain surgery
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of increased pressure inside the skull (that may lead to brain herniation) may include:
- High blood pressure
- Irregular or slow pulse
- Severe headache
- Weakness
- Cardiac arrest (no pulse)
- Loss of consciousness, coma
Coma
Decreased alertness is a state of reduced awareness and is often a serious condition. A coma is the most severe state of decreased alertness in which...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Loss of all brainstem reflexes (blinking, gagging, and pupils reacting to light)
-
Respiratory arrest (no breathing)
Respiratory arrest
Breathing that stops from any cause is called apnea. Slowed breathing is called bradypnea. Labored or difficult breathing is known as dyspnea....
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Wide (dilated) pupils and no movement in one or both eyes
Exams and Tests
A brain and nervous system exam shows changes in alertness. Depending on the severity of the herniation and the part of the brain that is being pressed on, there will be problems with one or more brain-related reflexes and nerve functions.
Tests may include:
-
X-ray of the skull and neck
X-ray
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan of the head
CT scan of the head
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
MRI scan of the head
MRI scan of the head
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood tests if an abscess or a bleeding disorder is suspected
Treatment
Brain herniation is a medical emergency. The goal of treatment is to save the person's life.
To help reverse or prevent a brain herniation, the medical team will treat increased swelling and pressure in the brain. Treatment may involve:
- Placing a drain into the brain to help remove cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Medicines to reduce swelling, especially if there is a brain tumor, such as mannitol, saline, or other diuretics
- Placing a tube in the airway (endotracheal intubation) and increasing the breathing rate to reduce the levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood
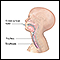
Endotracheal intubation
Endotracheal intubation is a medical procedure in which a tube is placed into the windpipe (trachea) through the mouth or nose. In most emergency si...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Removing blood or blood clots if they are raising pressure inside the skull and causing herniation
- Removing part of the skull to give the brain more room
Outlook (Prognosis)
People who have a brain herniation usually have a serious brain injury. They may already have a low chance of recovery due to the injury that caused the herniation. When herniation occurs, it further lowers the chance of recovery.
The outlook varies, depending on where in the brain the herniation occurs. Without treatment, death is likely.
There can be damage to parts of the brain that regulate breathing and blood flow. This can rapidly lead to death or brain death.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Brain death
- Permanent and significant neurologic problems
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call 911 or the local emergency number or take the person to a hospital emergency room if they develop decreased alertness or other symptoms, especially if there has been a head injury or if the person has a brain tumor or blood vessel problem.
Prevention
Prompt treatment of increased intracranial pressure and related disorders may reduce the risk for brain herniation.
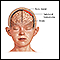
Increased intracranial pressure
Increased intracranial pressure is a rise in the pressure inside the skull that can result from or cause brain injury.
References
Beaumont A. Physiology of the cerebrospinal fluid and intracranial pressure. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 69.
Papa L, Goldberg SA. Head trauma. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 33.
Stippler M, Mahavadi A. Craniocerebral trauma. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 62.
-
Brain - illustration
The major areas of the brain have one or more specific functions.
Brain
illustration
-
Brain herniation - illustration
Brain herniation is a condition in which a portion of the brain is displaced because of increased pressure inside the skull. Increase in pressure results in progressive damage to brain tissue that may include life-threatening damage to the brainstem.
Brain herniation
illustration
-
Brain - illustration
The major areas of the brain have one or more specific functions.
Brain
illustration
-
Brain herniation - illustration
Brain herniation is a condition in which a portion of the brain is displaced because of increased pressure inside the skull. Increase in pressure results in progressive damage to brain tissue that may include life-threatening damage to the brainstem.
Brain herniation
illustration
Review Date: 8/19/2024
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.



