Erythrasma
Erythrasma is a long-term skin infection caused by a specific bacteria. It commonly occurs in skin folds.
Causes
Erythrasma is caused by the bacteria Corynebacterium minutissimum.
Erythrasma is more common in warm climates. You are more likely to develop this condition if you are overweight, older, or have diabetes.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
Symptoms
The main symptoms are reddish-brown slightly scaly patches with sharp borders. They may itch slightly. The patches occur in moist areas such as the groin, armpit, and skin folds.
Patches
A patch is a flat area of color change in the skin that is 0. 39 inches (in) or 1 centimeter (cm) or more wide. It is a type of skin lesion....
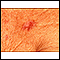
The patches often look similar to fungal infections, such as ringworm.
Ringworm
Ringworm is a skin infection due to a fungus. Often, there are several patches of ringworm on the skin at once. The medical name for ringworm is ti...

Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will check your skin and ask about the symptoms.
These tests can help diagnose erythrasma:
- Lab tests of scrapings from the skin patch
- Examination under a special lamp called a Wood lamp
Wood lamp
A Wood lamp examination is a test that uses ultraviolet (UV) light to look at the skin closely.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - A skin biopsy
Skin biopsy
A skin lesion biopsy is when a small amount of skin is removed so it can be examined under a microscope. The skin is tested to look for skin conditi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Your provider may suggest the following:
- Gentle scrubbing of the skin patches with antibacterial soap
- Antibiotic medicine applied to the skin
- Antibiotics taken by mouth
-
Laser treatment
Laser treatment
Laser surgery uses laser energy to treat the skin. Laser surgery can be used to treat skin diseases or cosmetic concerns such as sunspots or wrinkle...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Outlook (Prognosis)
The condition should go away after treatment.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of erythrasma.
Prevention
You may be able to reduce the risk of erythrasma if you:
- Bathe or shower often
- Keep your skin dry
- Wear clean clothes that absorb moisture
- Avoid very hot or damp conditions
- Maintain a healthy body weight
References
Barkham MC, Khong B. Erythrasma. In: Lebwohl MG, Heymann WR, Coulson IH, Murrell DF, eds. Treatment of Skin Disease. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2022:chap 77.
Dinulos JGH. Superficial fungal infections. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 13.
-
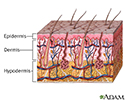
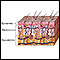
Skin layers - illustration
The skin is the largest organ of the body. The skin and its derivatives (hair, nails, sweat and oil glands) make up the integumentary system. One of the main functions of the skin is protection. It protects the body from external factors such as bacteria, chemicals, and temperature. The skin contains secretions that can kill bacteria and the pigment melanin provides a chemical pigment defense against ultraviolet light that can damage skin cells. Another important function of the skin is body temperature regulation. When the skin is exposed to a cold temperature, the blood vessels in the dermis constrict. This allows the blood which is warm, to bypass the skin. The skin then becomes the temperature of the cold it is exposed to. Body heat is conserved since the blood vessels are not diverting heat to the skin anymore. Among its many functions the skin is an incredible organ always protecting the body from external agents.
Skin layers
illustration
-
Skin layers - illustration
The skin is the largest organ of the body. The skin and its derivatives (hair, nails, sweat and oil glands) make up the integumentary system. One of the main functions of the skin is protection. It protects the body from external factors such as bacteria, chemicals, and temperature. The skin contains secretions that can kill bacteria and the pigment melanin provides a chemical pigment defense against ultraviolet light that can damage skin cells. Another important function of the skin is body temperature regulation. When the skin is exposed to a cold temperature, the blood vessels in the dermis constrict. This allows the blood which is warm, to bypass the skin. The skin then becomes the temperature of the cold it is exposed to. Body heat is conserved since the blood vessels are not diverting heat to the skin anymore. Among its many functions the skin is an incredible organ always protecting the body from external agents.
Skin layers
illustration
Review Date: 10/14/2024
Reviewed By: Elika Hoss, MD, Assistant Professor of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.