Rubella
Three day measles; German measlesRubella, also known as the German measles, is an infection in which there is a rash on the skin.
Congenital rubella is when a pregnant woman with rubella passes it to her baby that is still in her womb (uterus).
Congenital rubella
Congenital rubella is a condition that occurs in an infant whose mother is infected with the virus that causes German measles. Congenital means the ...
Causes
Rubella is caused by a virus that is spread through the air or by close contact.
A person with rubella may spread the disease to others from 1 week before the rash begins, until 1 to 2 weeks after the rash disappears.
Because the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine is given to most children, rubella is much less common now. Almost everyone who receives the vaccine has immunity to rubella. Immunity means that your body has built a defense to the rubella virus.
Measles-mumps-rubella
All content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC MMR (Measles, Mumps, & Rubella) Vaccine Information Statement (VIS): www. cdc. gov/vaccines/h...
In some adults, the vaccine may wear off. This means they are not fully protected. Women who may become pregnant and other adults may receive a booster shot.
Children and adults who were never vaccinated against rubella may also get this infection.
Symptoms
Children generally have few symptoms. Adults may have a fever, headache, general discomfort (malaise), and a runny nose before the rash appears. They may not notice the symptoms.
Malaise
Malaise is a general feeling of discomfort, illness, or lack of well-being.
Other symptoms may include:
- Bruising (rare)
- Inflammation of the eyes (bloodshot eyes)
- Muscle or joint pain
Exams and Tests
A nasal or throat swab may be sent for culture.
A blood test can be done to see if a person is protected against rubella. All women who may become pregnant should have this test. If the test is negative, they will receive the vaccine.
Treatment
There is no treatment for this disease.
Taking acetaminophen can help reduce fever.
Birth defects that occur with congenital rubella syndrome can be treated.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Rubella is most often a mild infection.
After an infection, people have immunity to the disease for the rest of their lives.
Possible Complications
Complications can occur in the unborn baby if the mother becomes infected during pregnancy. A miscarriage or stillbirth may occur. The child may be born with birth defects.
Stillbirth
A stillbirth is when a baby dies in the womb during the last 20 weeks of pregnancy. A miscarriage is a fetal loss in the first half of pregnancy...
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if:
- You are a woman of childbearing age and are unsure of whether you have been vaccinated against rubella
- You or your child develop a severe headache, stiff neck, earache, or vision problems during or after a case of rubella
- You or your child need to receive MMR immunization (vaccine)
Prevention
There is a safe and effective vaccine to prevent rubella. The rubella vaccine is recommended for all children. It is routinely given when children are 12 to 15 months old, but is sometimes given earlier during epidemics. A second vaccination (booster) is routinely given to children ages 4 to 6. MMR is a combination vaccine that protects against measles, mumps, and rubella.
Measles
Measles is a very contagious (easily spread) illness caused by a virus.
Mumps
Mumps is a contagious disease that leads to painful swelling of the salivary glands. The salivary glands produce saliva, a liquid that moistens food...
Women of childbearing age most often have a blood test to see if they have immunity to rubella. If they are not immune, women should avoid getting pregnant for 28 days after receiving the vaccine.
Those who should not get vaccinated include:
- Women who are pregnant.
- Anyone whose immune system is affected by cancer, corticosteroid medicines, or radiation treatment.
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleRadiation treatment
Radiation therapy uses high-powered radiation (such as x-rays or gamma rays), particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Great care is taken not to give the vaccine to a woman who is already pregnant. However, in the rare instances when pregnant women have been vaccinated, no problems have been detected in the infants.
References
Gans HA. Rubella. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 294.
Michaels MG, Williams JV. Infectious diseases. In: Zitelli, BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 13.
Winter AK, Moss WJ. Rubella. Lancet. 2022;399(10332):1336-1346. PMID: 35367004 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35367004/.
Wodi AP, Murthy N, McNally VV, Daley MF, Cineas S. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices Recommended Immunization Schedule for Children and Adolescents Aged 18 Years or Younger - United States, 2024. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024;73(1):6-10. PMID: 38206855 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38206855/.
-
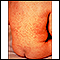
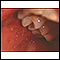
Rubella on an infant's back - illustration
Rubella is often called three-day measles. Because of the very effective vaccine, rubella is seldom seen today. The rubella vaccine is given in combination with measles (rubeola) and mumps. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Rubella on an infant's back
illustration
-
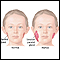
Rubella - illustration
Rubella is a contagious viral infection with mild symptoms associated with a rash, fever, headache and runny nose. It can be transmitted to a fetus by a mother with an active infection. Another name for rubella is German measles.
Rubella
illustration
-
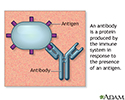
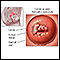
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
-
Rubella on an infant's back - illustration
Rubella is often called three-day measles. Because of the very effective vaccine, rubella is seldom seen today. The rubella vaccine is given in combination with measles (rubeola) and mumps. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Rubella on an infant's back
illustration
-
Rubella - illustration
Rubella is a contagious viral infection with mild symptoms associated with a rash, fever, headache and runny nose. It can be transmitted to a fetus by a mother with an active infection. Another name for rubella is German measles.
Rubella
illustration
-
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
Review Date: 1/1/2025
Reviewed By: Charles I. Schwartz, MD, FAAP, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, General Pediatrician at PennCare for Kids, Phoenixville, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.