Adrenal glands
The adrenal glands are two small triangle-shaped glands in the upper abdomen. One gland is located on top of each kidney.
Information
Each adrenal gland is about the size of the top part of the thumb. The outer part of the gland is called the cortex. It produces steroid hormones such as cortisol, aldosterone, and hormones that can be changed into testosterone. The inner part of the gland is called the medulla. It produces epinephrine and norepinephrine. These hormones are also called adrenaline and noradrenaline.
When the glands produce more or less hormones than normal, you can become sick. This might happen at birth or later in life.
The adrenal glands can be affected by many diseases, such as autoimmune disorders, infections, tumors, and bleeding. Some are permanent and some go away over time. Medicines can also affect the adrenal glands.
Autoimmune disorders
An autoimmune disease occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune di...
Tumors
A tumor is an abnormal growth of body tissue. Tumors can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
The pituitary, a small gland at the bottom of the brain, releases a hormone called ACTH that stimulates the adrenal cortex to make its hormones. Pituitary diseases can lead to problems with adrenal function.
Conditions related to adrenal gland problems include:
-
Addison disease, also called adrenal insufficiency -- an autoimmune disorder that causes the adrenal glands to not produce enough hormones
Addison disease
Addison disease is a disorder that causes the adrenal glands to not produce enough hormones.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia -- disorder in which the adrenal glands lack an enzyme needed to make certain hormones
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is the name given to a group of inherited disorders of the adrenal gland. Inherited means the traits are passed down ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cushing syndrome -- disorder that occurs when the body has a high level of the hormone cortisol
Cushing syndrome
Cushing syndrome is a disorder that occurs when your body has a high level of the hormone cortisol.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Diabetes mellitus (high blood sugar) caused by the adrenal gland making too much cortisol
Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Glucocorticoid medicines such as prednisone, methylprednisolone, dexamethasone, and hydrocortisone
-
Excessive or unwanted hair in women (hirsutism)
Hirsutism
Most of the time, women have fine hair above their lips and on their chin, chest, abdomen, or back. The growth of coarse dark hair in these areas (m...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hump behind shoulders (dorsocervical fat pad)
Hump behind shoulders
A hump on the upper back between the shoulder blades is an area of fat accumulation on the back of the neck. The medical name of this condition is d...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hypoglycemia -- low blood sugar
Hypoglycemia
Low blood sugar is a condition that occurs when the body's blood sugar (glucose) decreases and is too low. Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL (3. 9 mmol/L) i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Primary aldosteronism (Conn syndrome) -- disorder in which the adrenal gland releases too much of the hormone aldosterone
Primary aldosteronism
Hyperaldosteronism is a condition in which the adrenal gland releases too much of the hormone aldosterone into the blood. Hyperaldosteronism can be p...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Massive bilateral adrenal hemorrhage (Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome) -- failure of adrenal glands to function as a result of bleeding into the gland, usually associated with severe infection, called sepsis
Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome
Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome (WFS) is a group of symptoms that occur when the adrenal glands fail to function normally. This is caused by bleedi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Newell-Price JDC, Auchus RJ. The adrenal cortex. In: Melmed S, Auchus, RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 15.
Nieman LK. Adrenal cortex. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 208.
Standring S. Suprarenal (adrenal) gland. In: Standring S, ed. Gray's Anatomy. 42nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 70.
Young WF. Adrenal medulla, catecholamines, and pheochromocytoma. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 209.
-
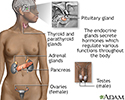
Endocrine glands - illustration
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the rate of metabolism in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
Endocrine glands
illustration
-
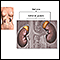
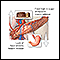
Adrenal glands - illustration
The adrenal glands are triangular-shaped and located on top of the kidneys. They produce steroid hormones such as aldosterone, cortisol, and precursor sex steroids that can be converted into estrogen and testosterone. They also produce the hormones adrenalin (epinephrine) and noradrenalin (norepinephrine).
Adrenal glands
illustration
-
Endocrine glands - illustration
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the rate of metabolism in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
Endocrine glands
illustration
-
Adrenal glands - illustration
The adrenal glands are triangular-shaped and located on top of the kidneys. They produce steroid hormones such as aldosterone, cortisol, and precursor sex steroids that can be converted into estrogen and testosterone. They also produce the hormones adrenalin (epinephrine) and noradrenalin (norepinephrine).
Adrenal glands
illustration
Review Date: 5/20/2024
Reviewed By: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.