Bile
Bile is a fluid that is made and released by the liver and stored in the gallbladder.
Bile helps with digestion. It breaks down fats into fatty acids, which can be taken into the body by the digestive tract.
Bile contains:
- Mostly cholesterol
- Bile acids (also called bile salts)
- Bilirubin (a breakdown product or red blood cells)
It also contains:
- Water
- Body salts (such as potassium and sodium)
- Copper and other metals (attached to proteins)
References
Hall JE, Hall ME. Secretory functions of the alimentary tract. In: Hall JE, Hall ME, eds. Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 65.
Radkani P, Hawksworth J, Fishbein T. Biliary system. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 55.
-
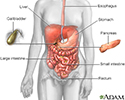
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
Bile produced in the liver - illustration
The biliary organs and duct system that creates, transports, stores, and releases bile into the duodenum for digestion includes the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts (named the cystic, hepatic, common, and pancreatic duct).
Bile produced in the liver
illustration
-
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
Bile produced in the liver - illustration
The biliary organs and duct system that creates, transports, stores, and releases bile into the duodenum for digestion includes the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts (named the cystic, hepatic, common, and pancreatic duct).
Bile produced in the liver
illustration
Review Date: 7/23/2024
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.