Neurologic deficit
A neurologic deficit refers to abnormal neurologic function of a body area. This altered function is due to injury of the brain, spinal cord, muscles, or nerves that feed the affected area.
Examples include:
-
Abnormal reflexes
Abnormal reflexes
Reflexes are responses that occur when the body receives a certain stimulus. The Babinski reflex occurs after the sole of the foot has been firmly s...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Inability to speak
-
Decreased sensation
Decreased sensation
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Loss of balance or coordination
- Mental function problems, such as memory loss or difficulty with thought processing
- Vision changes
- Walking problems
- Weakness of the face, arms or legs
References
De Luca GC, Griggs RC, Johnston SC. Approach to the patient with neurologic disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 366.
Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Newman NJ, Pomeroy SL. Diagnosis of neurological disease. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 1.
Klatt EC. The central nervous system. In: Klatt EC, ed. Robbins and Cotran Atlas of Pathology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 19.
-
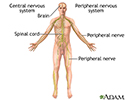
Nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes all peripheral nerves.
Nervous system
illustration
Review Date: 2/11/2025
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.