Endocrine glands
Endocrine glands release (secrete) hormones into the bloodstream.
The endocrine glands include the:
-
Adrenal
Adrenal
The adrenal glands are two small triangle-shaped glands in the upper abdomen. One gland is located on top of each kidney.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hypothalamus
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is an area of the brain that produces hormones that regulate:Body temperatureHeart rateHungerMoodRelease of hormones from many gland...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas
- Ovaries
- Parathyroid
- Pineal
- Pituitary
-
Testes
Testes
The testes are 2 egg-shaped male reproductive organs located in the scrotum. They produce sperm and the male hormone, testosterone.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Thyroid
Information
Hypersecretion is when an excess of one or more hormone is secreted from a gland. Hyposecretion is when the amount of hormones that are released is too low.
There are many types of disorders that can result when too much or too little of a hormone is released.
Disorders that may be associated with abnormal hormone product from a particular gland include:
Adrenal:
-
Addison disease
Addison disease
Addison disease is a disorder that causes the adrenal glands to not produce enough hormones.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Adrenogenital syndrome or adrenocortical hyperplasia
Adrenogenital syndrome
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is the name given to a group of inherited disorders of the adrenal gland. Inherited means the traits are passed down ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cushing syndrome
Cushing syndrome
Cushing syndrome is a disorder that occurs when your body has a high level of the hormone cortisol.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor of adrenal gland tissue that typically arises from the adrenal gland. It results in the release of too much epineph...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Pancreas:
-
Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia
Low blood sugar is a condition that occurs when the body's blood sugar (glucose) decreases and is too low. Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL (3. 9 mmol/L) i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Parathyroid:
- Low or high blood calcium level
- Tetany (abnormal cramping of muscles)
-
Renal calculi (kidney stones)
Renal calculi
A kidney stone is a solid mass made up of tiny crystals. One or more stones can be in the kidney or ureter at the same time.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Excessive loss of minerals from bone (osteoporosis)
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break (fracture).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Pituitary:
-
Growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency means the pituitary gland does not make enough growth hormone.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Acromegaly
Acromegaly
Acromegaly is a condition in which there is too much growth hormone (GH) in your body.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Gigantism
Gigantism
Gigantism is abnormal growth due to an excess of growth hormone (GH) during childhood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus (DI) is an uncommon condition in which the kidneys are unable to prevent the excretion of water. DI is not the same as diabetes me...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cushing disease
Cushing disease
Cushing disease is a condition in which the pituitary gland releases too much adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). The pituitary gland is an organ of...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Testes and ovaries:
- Lack of sex development (unclear genitalia)
Thyroid:
-
Congenital hypothyroidism
Congenital hypothyroidism
Neonatal hypothyroidism is decreased thyroid hormone production in a newborn. In very rare cases, no thyroid hormone is produced. The condition is ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Myxedema
Myxedema
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. This condition is often called underactive thyroid....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Goiter
Goiter
A simple goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland. It is usually not a tumor or cancer.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Thyrotoxicosis
Thyrotoxicosis
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. The condition is often called overactive thyroid.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Clemmons DR, Nieman LK. Approach to the patient with endocrine disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 202.
Jameson JL. Principles of endocrinology. In: Robertson RP, ed. DeGroot's Endocrinology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 1.
Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Kopp PA, Rosen CJ, et al. Principles of endocrinology. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Rosen CJ, Kopp PA, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 15th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 1.
-
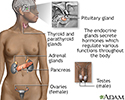
Endocrine glands - illustration
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the rate of metabolism in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
Endocrine glands
illustration
-
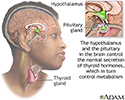
Brain-thyroid link - illustration
Although the thyroid gland releases the hormones which govern growth and metabolism, the brain (the pituitary and the hypothalamus) manages the release and the balance of the amount of hormones circulated.
Brain-thyroid link
illustration
-
Endocrine glands - illustration
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the rate of metabolism in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
Endocrine glands
illustration
-
Brain-thyroid link - illustration
Although the thyroid gland releases the hormones which govern growth and metabolism, the brain (the pituitary and the hypothalamus) manages the release and the balance of the amount of hormones circulated.
Brain-thyroid link
illustration
Review Date: 4/24/2025
Reviewed By: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.