Genes
A gene is a short piece of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Genes tell the body how to build specific proteins. There are about 20,000 genes in each cell of the human body. Together, they make up the blueprint for the human body and how it works.
Proteins
Proteins are the building blocks of life. Every cell in the human body contains protein. The basic structure of protein is a chain of amino acids. ...

A person's genetic makeup is called a genotype.
Information
Genes are made of DNA. Strands of DNA make up part of your chromosomes. Chromosomes have matching strands of DNA that make specific genes. Except for the sex chromosomes (X and Y), chromosomes are paired so there are 2 genes, 1 on each chromosome. The gene occurs in the same position on each chromosome.
Chromosomes
Chromosomes are structures found in the center (nucleus) of cells that carry long pieces of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA is the material that ho...

Genetic traits, such as eye color, are dominant or recessive:
- Dominant traits are controlled by 1 gene in the pair of chromosomes.
- Recessive traits need both genes in the gene pair to work together.
Many personal characteristics, such as height, are determined by more than 1 gene. However, some diseases, such as sickle cell anemia, can be caused by a change in a single gene.
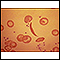
Sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell disease is a disorder passed down through families. The red blood cells that are normally shaped like a disk take on a sickle or crescen...
Change in a single gene
Autosomal dominant is one of many ways that a genetic trait or disorder can be passed down through families. In an autosomal dominant disease, if you...

References
Biesecker LG. Clinical genomics-genome structure and variation. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 32.
Taber's Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company; 2021. www.tabers.com/tabersonline/view/Tabers-Dictionary/729952/all/gene. Accessed April 1, 2025.
-
Chromosomes and DNA - illustration
Humans typically have 23 pairs of chromosomes, or 46 chromosomes in total. Chromosomes are made up of long strands of DNA, which contain all the body's genes.
Chromosomes and DNA
illustration
Review Date: 4/1/2025
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor Emeritus, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


