Hysterectomy
Vaginal hysterectomy; Abdominal hysterectomy; Supracervical hysterectomy; Radical hysterectomy; Removal of the uterus; Laparoscopic hysterectomy; Laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy; LAVH; Total laparoscopic hysterectomy; TLH; Laparoscopic supracervical hysterectomy; Robotically assisted hysterectomyHysterectomy is surgery to remove a woman's womb (uterus). The uterus is a hollow muscular organ that nourishes the developing baby during pregnancy.
Description
You may have all or part of the uterus removed during a hysterectomy. The fallopian tubes and ovaries may also be removed.
There are many different ways to perform a hysterectomy. It may be done through:
- A surgical cut in the belly (called an open or abdominal hysterectomy)
- Three to four small surgical cuts in the belly and then using a laparoscope
- A surgical cut in the vagina, aided by the use of a laparoscope (called a vaginal hysterectomy)
- A surgical cut in the vagina without the use of a laparoscope (called a vaginal hysterectomy)
- Three to four small surgical cuts in the belly, in order to perform robotic surgery
You and your surgeon will decide which type of procedure. The choice will depend on your medical history and the reason for the surgery.
Why the Procedure is Performed
There are many reasons a woman may need a hysterectomy, including:
-
Adenomyosis, a condition that causes heavy, painful periods
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis is a thickening of the walls of the uterus. It occurs when endometrial tissue grows into the outer muscular walls of the uterus. Endome...
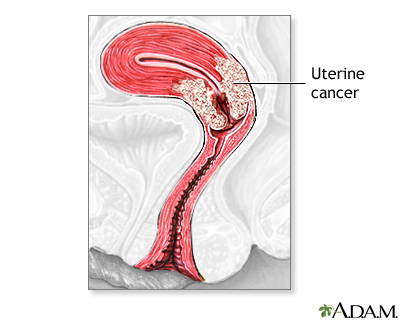
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Cancer of the uterus, most often endometrial cancer
Endometrial cancer
Endometrial cancer is cancer that starts in the endometrium, the lining of the uterus (womb).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
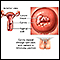
Cancer of the cervix or changes in the cervix called cervical dysplasia that may lead to cancer
Cancer of the cervix
Cervical cancer is cancer that starts in the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus (womb) that opens at the top of the vagina.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
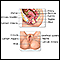
Cancer of the ovary
Cancer of the ovary
Ovarian cancer is cancer that starts in the ovaries. The ovaries are the female reproductive organs that produce eggs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Long-term (chronic) pelvic pain
- Severe endometriosis that does not get better with other treatments
Endometriosis
Endometriosis occurs when cells from the lining of your womb (uterus) grow in other areas of your body. This can cause pain, heavy vaginal bleeding,...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Severe, long-term vaginal bleeding that is not controlled with other treatments
- Slipping of the uterus into the vagina (uterine prolapse)
Uterine prolapse
Uterine prolapse occurs when the womb (uterus) drops down and presses into the vaginal area.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tumors in the uterus, such as uterine fibroids
Uterine fibroids
Uterine fibroids are tumors that grow in a woman's womb (uterus). These growths are typically not cancerous (benign), and do not become cancerous....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Uncontrolled bleeding during childbirth
- Severe infection involving the uterus (for example, pelvic inflammatory disease)
Hysterectomy is a major surgery. Some conditions can be treated with medicines or less invasive procedures such as:
-
Uterine artery embolization
Uterine artery embolization
Uterine artery embolization (UAE) is a procedure to treat fibroids without surgery. Uterine fibroids are noncancerous (benign) tumors that develop i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Endometrial ablation
- Using birth control pills
- Using pain medicines
- Using an IUD (intrauterine device) that releases the hormone progestin
-
Pelvic laparoscopy
Pelvic laparoscopy
Pelvic laparoscopy is surgery to examine the pelvic organs. It uses a viewing tool called a laparoscope. The surgery is also used to treat certain ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
Risks of any surgery are:
- Allergic reactions to medicines
-
Breathing problems
Breathing problems
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
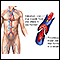
Blood clots, which may cause death if they travel to the lungs
Blood clots
Blood clots are clumps that occur when blood hardens from a liquid to a solid. A blood clot that forms inside one of your veins or arteries is calle...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
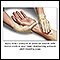
Bleeding
Bleeding
Bleeding is the loss of blood. Bleeding may be:Inside the body (internal)Outside the body (external)Bleeding may occur:Inside the body when blood le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection
- Injury to nearby body areas
Risks of a hysterectomy are:
- Injury to the bladder or ureters
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Early menopause if the ovaries are removed
- Decreased interest in sex
- Increased risk of heart disease if the ovaries are removed before menopause
Before the Procedure
Before deciding to have a hysterectomy, ask your health care provider what to expect after the procedure. Many women notice changes in their body and in how they feel about themselves after a hysterectomy. Talk with your provider, family, and friends about these possible changes before you have surgery.
Tell your health care team about all the medicines you are taking. These include herbs, supplements, and other medicines you bought without a prescription.
During the days before the surgery:
- You may be asked to stop taking aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), clopidogrel (Plavix), warfarin (Coumadin), and any other medicines like these.
- Ask your surgeon which medicines you should still take on the day of your surgery.
- If you smoke, try to stop. Ask your provider for help quitting.
On the day of your surgery:
- You will most often be asked not to drink or eat anything for 8 hours before the surgery.
- Take any medicines your provider told you to take with a small sip of water.
- Arrive at the hospital on time.
After the Procedure
After surgery, you will be given pain medicines.
You may also have a tube, called a catheter, inserted into your bladder to pass urine. Most of the time, the catheter is removed before leaving the hospital.
You will be asked to get up and move around as soon as possible after surgery. This helps prevent blood clots from forming in your legs and speeds recovery.
Blood clots
Blood clots are clumps that occur when blood hardens from a liquid to a solid. A blood clot that forms inside one of your veins or arteries is calle...

You will be asked to get up to use the bathroom as soon as you are able. You may return to a normal diet as soon as you can without causing nausea and vomiting.
How long you stay in the hospital depends on the type of hysterectomy.
- You can likely go home the next day when surgery is done through the vagina, with a laparoscope, or after robotic surgery.
- When a larger surgical cut (incision) in the abdomen is made, you may need to stay in the hospital for 1 to 2 days. You may need to stay longer if the hysterectomy is done because of cancer.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How long it takes you to recover depends on the type of hysterectomy. Average recovery times are:
-
Abdominal hysterectomy: 4 to 6 weeks
Abdominal hysterectomy
You were in the hospital to have surgery to remove your uterus. The fallopian tubes and ovaries may also have been removed. A surgical cut was made...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Vaginal hysterectomy: 3 to 4 weeks
Vaginal hysterectomy
You were in the hospital to have a vaginal hysterectomy. This article tells you what to expect and how to care for yourself when you return home aft...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Robot-assisted or total laparoscopic hysterectomy: 2 to 4 weeks
Robot-assisted or total laparoscopic hy...
You were in the hospital to have surgery to remove your uterus. The fallopian tubes and ovaries may also have been removed. A laparoscope (a thin t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
A hysterectomy will cause menopause if you also have your ovaries removed. Removal of the ovaries can also lead to a decreased sex drive. Your doctor may recommend estrogen replacement therapy. Discuss with your provider the risks and benefits of this therapy.
Estrogen replacement therapy
Hormone therapy (HT) uses one or more hormones to treat symptoms of menopause. HT uses estrogen, progestin (a type of progesterone), or both. Somet...
If the hysterectomy was done for cancer, you may need further treatment.
References
Committee on Gynecologic Practice. Committee opinion no 701: choosing the route of hysterectomy for benign disease. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;129(6):e155-e159. PMID: 28538495 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28538495/.
Karram MM. Vaginal hysterectomy. In: Baggish MS, Karram MM, eds. Atlas of Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 51.
Prescott LS, Yunker AC, Alvarez R. Gynecologic surgery. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 71.
Thakar R. Is the uterus a sexual organ? Sexual function following hysterectomy. Sex Med Rev. 2015;3(4):264-278. PMID: 27784599 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27784599/.
-
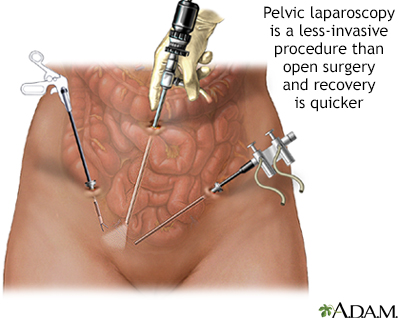
Pelvic laparoscopy - illustration
Laparoscopy is performed when less-invasive surgery is desired. It is also called Band-Aid surgery because only small incisions need to be made to accommodate the small surgical instruments that are used to view the abdominal contents and perform the surgery.
Pelvic laparoscopy
illustration
-
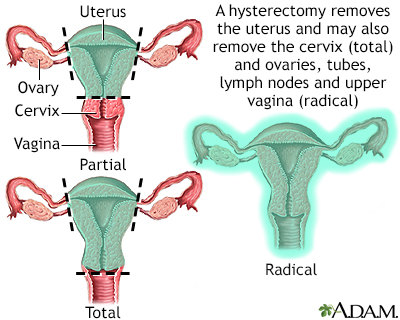
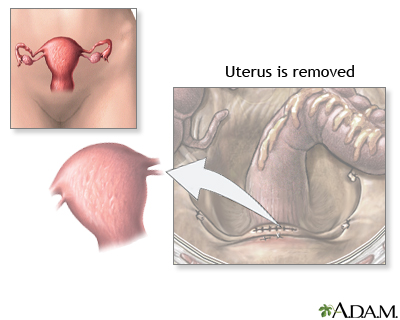
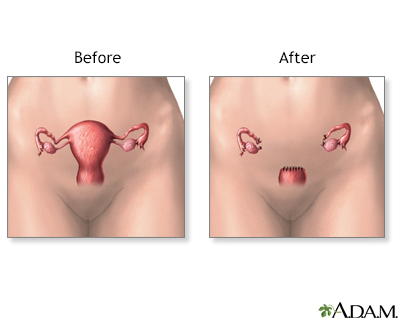
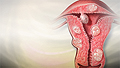
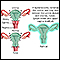
Hysterectomy - illustration
Hysterectomy is surgical removal of the uterus, resulting in inability to become pregnant. This surgery may be done for a variety of reasons including, but not restricted to, chronic pelvic inflammatory disease, uterine fibroids and cancer. A hysterectomy may be done through an abdominal or a vaginal incision.
Hysterectomy
illustration
-
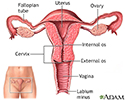
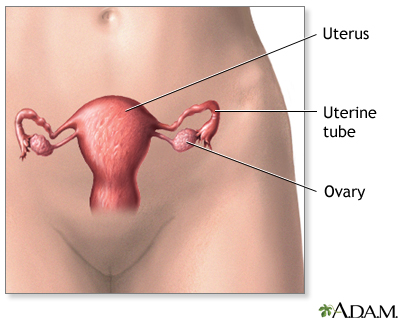
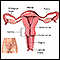
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
-
Hysterectomy - Series
Presentation
-
Pelvic laparoscopy - illustration
Laparoscopy is performed when less-invasive surgery is desired. It is also called Band-Aid surgery because only small incisions need to be made to accommodate the small surgical instruments that are used to view the abdominal contents and perform the surgery.
Pelvic laparoscopy
illustration
-
Hysterectomy - illustration
Hysterectomy is surgical removal of the uterus, resulting in inability to become pregnant. This surgery may be done for a variety of reasons including, but not restricted to, chronic pelvic inflammatory disease, uterine fibroids and cancer. A hysterectomy may be done through an abdominal or a vaginal incision.
Hysterectomy
illustration
-
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
-
Hysterectomy - Series
Presentation
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.