Pelvic laparoscopy
Celioscopy; Band-aid surgery; Pelviscopy; Gynecologic laparoscopy; Exploratory laparoscopy - gynecologicPelvic laparoscopy is surgery to examine the pelvic organs. It uses a viewing tool called a laparoscope. The surgery is also used to treat certain diseases of the pelvic organs.
Description
While you are deep asleep and pain-free under general anesthesia, the doctor makes a half-inch (1.25 centimeters) surgical cut in the skin below the belly button. Carbon dioxide gas is pumped into the abdomen to help the surgeon see the organs more easily.
The laparoscope, an instrument that looks like a small telescope with a light and a video camera, is inserted so the surgeon can view the area.
Other instruments may be inserted through other small cuts in the lower abdomen. While watching a video monitor, the surgeon is able to:
- Take tissue samples (biopsy)
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Look for the cause of any symptoms
- Remove scar tissue or other abnormal tissue, such as from endometriosis
Endometriosis
Endometriosis occurs when cells from the lining of your womb (uterus) grow in other areas of your body. This can cause pain, heavy vaginal bleeding,...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Repair or remove part or all of the ovaries or uterine tubes
- Repair or remove parts of the uterus
- Do other surgical procedures (such as appendectomy, removing lymph nodes)
Appendectomy
An appendectomy is surgery to remove the appendix.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
After the laparoscopy, the carbon dioxide gas is released, and the cuts are closed.
Why the Procedure is Performed
Laparoscopy uses a smaller surgical cut than open surgery. Most people who have this procedure are able to return home the same day. The smaller incision also means that the recovery is faster. There is less blood loss with laparoscopic surgery and less pain after surgery.
Pelvic laparoscopy is used both for diagnosis and treatment. It may be recommended for:
- An abnormal pelvic mass or ovarian cyst found using pelvic ultrasound
Pelvic ultrasound
Transvaginal ultrasound is a test used to look at a woman's uterus, ovaries, tubes, cervix, and pelvic area. Transvaginal means across or through the...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cancer (ovarian, endometrial, or cervical) to see if it has spread, or to remove nearby lymph nodes or tissue
Ovarian
Ovarian cancer is cancer that starts in the ovaries. The ovaries are the female reproductive organs that produce eggs.
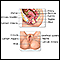 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleEndometrial
Endometrial cancer is cancer that starts in the endometrium, the lining of the uterus (womb).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic (long-term) pelvic pain, if no other cause has been found
-
Ectopic (tubal) pregnancy
Ectopic (tubal) pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that occurs outside the womb (uterus).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Endometriosis
- Difficulty getting pregnant or having a baby (infertility)
- Sudden, severe pelvic pain
A pelvic laparoscopy may also be done to:
- Remove your uterus (hysterectomy)
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is surgery to remove a woman's womb (uterus). The uterus is a hollow muscular organ that nourishes the developing baby during pregnancy...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Remove uterine fibroids (myomectomy)
- "Tie" your tubes (tubal ligation/sterilization)
Risks
Risks of any pelvic surgery include:
- Bleeding
- Blood clots in the leg or pelvic veins, which could travel to the lungs and, rarely, be fatal
- Breathing problems
- Damage to nearby organs and tissues
- Heart problems
- Infection
Laparoscopy is safer than an open procedure for correcting the problem.
Before the Procedure
Always tell your health care provider:
- If you are or could be pregnant
- What medicines you are taking, even drugs, herbs, or supplements you bought without a prescription
During the days before surgery:
- You may be asked to stop taking aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), warfarin (Coumadin), and any other medicines that make it hard for your blood to clot.
- Ask your surgeon which medicines you can still take on the day of your surgery.
- If you smoke, try to stop. Ask your provider for help.
- Arrange for someone to drive you home after surgery.
On the day of your surgery:
- You will usually be asked not to drink or eat anything after midnight the night before your surgery, or 8 hours before your surgery.
- Take the medicines your surgeon told you to take with a small sip of water.
- Your surgeon will tell you when to arrive at the hospital or clinic.
After the Procedure
You will spend some time in a recovery area as you wake up from the anesthesia.
Many people are able to go home the same day as the procedure. Sometimes, you may need to stay overnight, depending on what surgery was done using the laparoscope.
The gas pumped into the abdomen may cause abdominal discomfort for 1 to 2 days after the procedure. Some people feel neck and shoulder pain for several days after a laparoscopy because the carbon dioxide gas irritates the diaphragm. As the gas is absorbed, this pain will go away. Lying down can help decrease the pain.
You will get a prescription for pain medicine or be told what over-the-counter pain medicines you can take.
You may go back to your normal activities within 1 to 2 days. However, DO NOT lift anything over 10 pounds (4.5 kilograms) for 3 weeks after surgery to decrease your risk of getting a hernia in your incisions.
Hernia
A hernia is a sac formed by the lining of the abdominal cavity (peritoneum). The sac comes through a hole or weak area in the strong layer of the be...
Depending on what procedure is done, you can usually begin sexual activities again as soon as any bleeding has stopped. If you have had a hysterectomy, you need to wait a longer period before having sexual intercourse again. Ask your surgeon what is recommended for the procedure you are having.
Contact your surgeon if you have:
- Bleeding from the vagina
- Fever that does not go away
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe abdominal pain
References
Burney RO, Giudice LC. Endometriosis. In: Robertson RP, ed. DeGroot's Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 125.
Cohen JG, Bixel K, Backes FJ. Role of minimally invasive surgery in gynecologic malignancies. In: Creasman WT, Mutch DG, Mannel RS, Tewari KS, eds. DiSaia and Creasman Clinical Gynecologic Oncology. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 20.
Patel RM, Kaler KS, Landman J. Fundamentals of laparoscopic and robotic urologic surgery. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 14.
Raymond L, Lentz GM. Endoscopy in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 10.
-
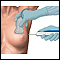
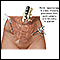
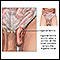
Pelvic laparoscopy - illustration
Laparoscopy is performed when less-invasive surgery is desired. It is also called Band-Aid surgery because only small incisions need to be made to accommodate the small surgical instruments that are used to view the abdominal contents and perform the surgery.
Pelvic laparoscopy
illustration
-
Endometriosis - illustration
Endometriosis is the condition in which the tissue that normally lines the uterus (endometrium) grows on other areas of the body causing pain and irregular bleeding.
Endometriosis
illustration
-
Pelvic adhesions - illustration
Pelvic adhesions are bands of scar-like tissue that form between two surfaces inside the body. Inflammation from infection, surgery, or trauma can cause tissues to bond to other tissues or organs.
Pelvic adhesions
illustration
-
Ovarian cyst - illustration
An ovarian cyst is a sac filled with fluid, or a semisolid material, that develops on or within the ovary. Ovarian cysts are relatively common and usually disappear without treatment.
Ovarian cyst
illustration
-
Pelvic laparoscopy - illustration
Laparoscopy is performed when less-invasive surgery is desired. It is also called Band-Aid surgery because only small incisions need to be made to accommodate the small surgical instruments that are used to view the abdominal contents and perform the surgery.
Pelvic laparoscopy
illustration
-
Endometriosis - illustration
Endometriosis is the condition in which the tissue that normally lines the uterus (endometrium) grows on other areas of the body causing pain and irregular bleeding.
Endometriosis
illustration
-
Pelvic adhesions - illustration
Pelvic adhesions are bands of scar-like tissue that form between two surfaces inside the body. Inflammation from infection, surgery, or trauma can cause tissues to bond to other tissues or organs.
Pelvic adhesions
illustration
-
Ovarian cyst - illustration
An ovarian cyst is a sac filled with fluid, or a semisolid material, that develops on or within the ovary. Ovarian cysts are relatively common and usually disappear without treatment.
Ovarian cyst
illustration
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.





