Appendectomy
Appendix removal; Surgery - appendectomy; Appendicitis - appendectomyAn appendectomy is surgery to remove the appendix.
Description
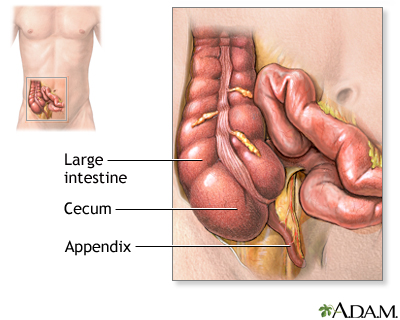
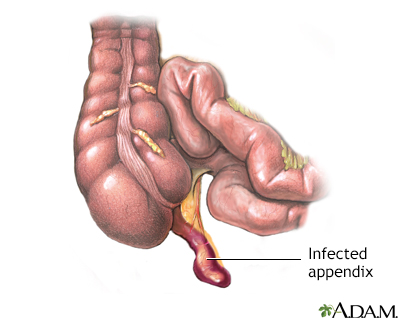
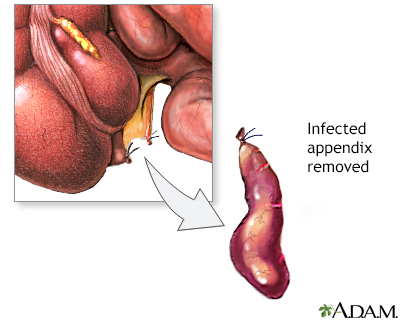
The appendix is a small, finger-shaped organ that branches off from the first part of the large intestine (colon). When it becomes swollen (inflamed) or infected, the condition is called appendicitis. When you have appendicitis, your appendix may need to be removed. An appendix that has a hole in it can leak and infect the entire abdomen area. This can be life threatening.
Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a condition in which your appendix gets inflamed. The appendix is a small pouch attached to the end of the large intestine.
Appendectomy is done using either:
-
Spinal anesthesia -- Medicine is put into your lower back to make you numb below your waist. You will also get medicine to make you sleepy.
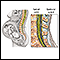
Spinal anesthesia
Spinal and epidural anesthesia are procedures that deliver medicines that numb parts of your body to block pain. They are given through shots in or ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
General anesthesia -- You will be asleep and not feel any pain during the surgery.
General anesthesia
General anesthesia is treatment with certain medicines that puts you into a deep sleep-like state so you do not feel pain during surgery. After you ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
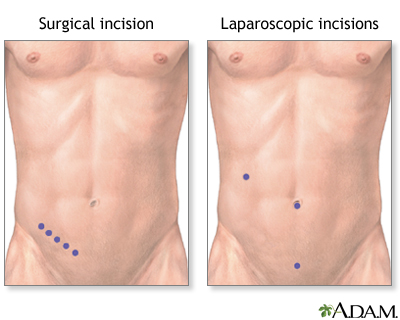
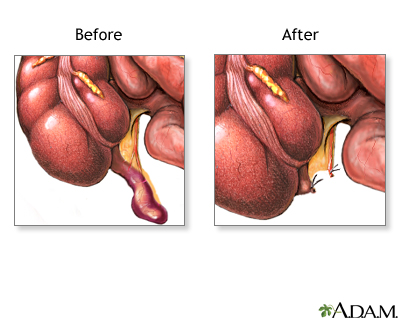
Your surgeon may make a small cut in the lower right side of your belly area and remove the appendix.
Your appendix can also be removed using small surgical cuts and a camera. This is called a laparoscopic appendectomy.
If your appendix broke open or a pocket of infection (abscess) formed, your abdomen may be washed out during surgery. A small tube may be left in the belly area to help drain out fluids or pus.
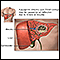
Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus in any part of the body. In most cases, the area around an abscess is swollen and inflamed.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
An appendectomy is done for appendicitis. The condition can be hard to diagnose, especially in children, older people, and women of childbearing age.
Most often, the first symptom is pain around your belly button:
- The pain may be mild at first, but it becomes sharp and severe.
- The pain often moves into your right lower abdomen and becomes more focused in this area.
Other symptoms include:
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Fever (usually not very high)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Reduced appetite
If you have symptoms of appendicitis, seek medical help right away. Do not use heating pads, enemas, laxatives, or other home treatments to try to relieve symptoms.
Your health care provider will examine your abdomen and may perform a rectal exam and pelvic exam. Other tests may be done:
- Blood tests, including a white blood cell (WBC) count, may be done to check for infection.
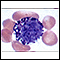
White blood cell (WBC) count
A WBC count is a blood test to measure the number of white blood cells (WBCs) in the blood. It is a part of a complete blood count (CBC). WBCs are a...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Your provider may order a CT scan or ultrasound to determine if the appendix is the cause of the problem since other illnesses can cause the same or similar symptoms.
CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
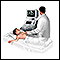
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleUltrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of organs and structures inside the body.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The goal is to remove an infected appendix before it breaks open (ruptures). After reviewing your symptoms and the results of the physical exam and medical tests, your surgeon will decide whether you need surgery.
Risks
Risks of anesthesia and surgery in general include:
- Reactions to medicines
- Problems breathing
- Bleeding, blood clots, or infection
Risks of an appendectomy after a ruptured appendix include:
- Buildup of pus (abscess), which may need draining and antibiotics
- Infection of the incision
After the Procedure
Most people leave the hospital in 1 to 2 days after surgery. You can go back to your normal activities within a few weeks after leaving the hospital though it may take several weeks to get back to your normal energy level.
If you had laparoscopic surgery, you will likely recover quickly. Recovery is slower and more complicated if your appendix has broken open or an abscess has formed.
Living without an appendix causes no known health problems.
References
Quick CRG, Biers SM, Arulampalam THA. Appendicitis. In: Quick CRG, Biers SM, Arulampalam THA, eds. Essential Surgery: Problems Diagnosis and Management. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2020:chap 26.
Richmond B. The appendix. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 51.
Rosenthal MD, Sarosi GS. Appendicitis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 120.
-
Anatomical landmarks adult - front - illustration
There are three body views (front, back, and side) that can help you to identify a specific body area. The labels show areas of the body which are identified either by anatomical or by common names. For example, the back of the knee is called the “popliteal fossa,” while the “flank” is an area on the side of the body.
Anatomical landmarks adult - front
illustration
-
Appendectomy - series
Presentation
-
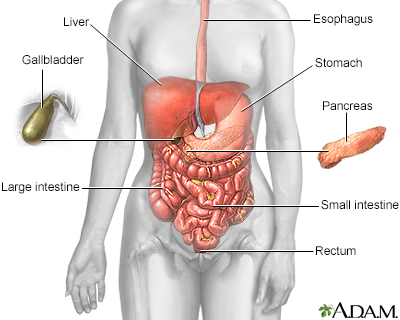
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
Anatomical landmarks adult - front - illustration
There are three body views (front, back, and side) that can help you to identify a specific body area. The labels show areas of the body which are identified either by anatomical or by common names. For example, the back of the knee is called the “popliteal fossa,” while the “flank” is an area on the side of the body.
Anatomical landmarks adult - front
illustration
-
Appendectomy - series
Presentation
-
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Debra G. Wechter, MD, FACS, General Surgery Practice Specializing in Breast Cancer, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.