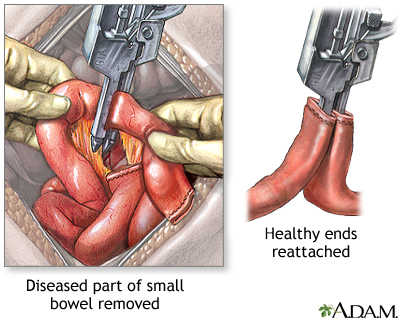
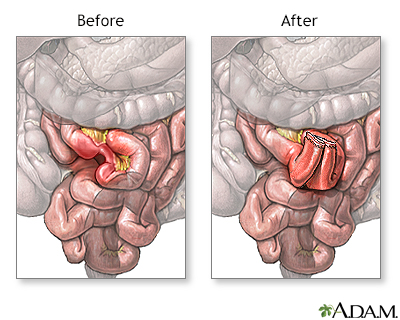
Small bowel resection
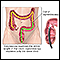
Small intestine surgery; Bowel resection - small intestine; Resection of part of the small intestine; EnterectomySmall bowel resection is surgery to remove a part of your small bowel. It is done when part of your small bowel is blocked or diseased.
The small bowel is also called the small intestine. Most digestion (breaking down and absorbing nutrients) of the food you eat takes place in the small intestine.
Description
You will receive general anesthesia at the time of your surgery. This will keep you asleep and pain-free.
General anesthesia
General anesthesia is treatment with certain medicines that puts you into a deep sleep-like state so you do not feel pain during surgery. After you ...
The surgery can be performed laparoscopically, with a robot, or open surgery.
If you have laparoscopic or robotic surgery:
- Your surgeon makes 3 to 5 small cuts (incisions) in your lower belly. A medical device called a laparoscope is inserted through one of the cuts. The scope is a thin, lighted tube with a camera on the end. It lets the surgeon see inside your belly. Other medical instruments are inserted through the other cuts.
- A cut of about 2 to 3 inches (in) or 5 to 7.6 centimeters (cm) may also be made if your surgeon needs to put their hand inside your belly to feel the intestine or remove the diseased segment.
- Your belly is filled with a harmless gas to expand it. This makes it easier for your surgeon to see and work.
- The diseased part of your small intestine is located and removed.
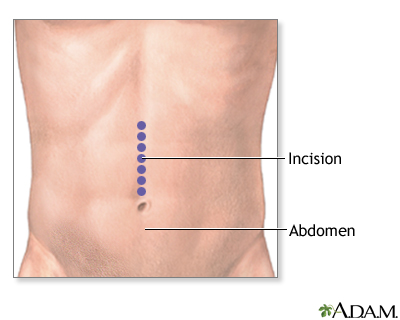
If you have open surgery:
- The surgeon makes a cut of 6 to 8 in (15.2 to 20.3 cm) in your mid-belly.
- The diseased part of your small intestine is located and removed.
In both kinds of surgery, the next steps are:
- If there is enough healthy small intestine left, the ends are stitched or stapled together. This is called an anastomosis. Most patients have this done.
- If there is not enough healthy small intestine to reconnect, your surgeon makes an opening called a stoma through the skin of your belly. The small intestine is attached to the outer wall of your belly. Stool will go through the stoma into a drainage bag outside your body. This is called an ileostomy. The ileostomy may be either short-term or permanent.
Ileostomy
An ileostomy is used to move waste out of the body. This surgery is done when the colon or rectum is not working properly. The word "ileostomy" come...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Small bowel resection usually takes 1 to 4 hours.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
Small bowel resection is used to treat:
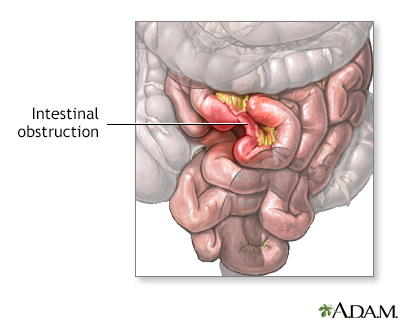
- A blockage in the intestine caused by scar tissue or congenital (from birth) deformities
Blockage in the intestine
Intestinal obstruction is a partial or complete blockage of the bowel. The contents of the intestine cannot pass through it.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bleeding, infection, or ulcers caused by inflammation of the small intestine from conditions such as Crohn disease
Ulcers
An ulcer is a crater-like sore on the skin or mucous membrane. Ulcers form when the top layers of skin or tissue have been removed. They can occur ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCrohn disease
Crohn disease is a disease where parts of the digestive tract become inflamed. It most often involves the lower end of the small intestine and the be...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
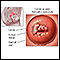
Cancer
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Carcinoid tumor
Carcinoid tumor
Carcinoid syndrome is a group of symptoms associated with carcinoid tumors. These are tumors most often of the small intestine, colon, appendix, pan...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Injuries to the small intestine
-
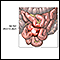
Meckel diverticulum (a pouch on the wall of the lower part of the intestine that is present at birth)
Meckel diverticulum
A Meckel diverticulum is a pouch on the wall of the lower part of the small intestine that is present at birth (congenital). The diverticulum may co...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Noncancerous (benign) tumors
- Precancerous polyps
- Foreign object in the small bowel
Risks
Risks of anesthesia and surgery in general are:
- Reactions to medicines
- Breathing problems
- Blood clots, bleeding, infection
- Nausea and vomiting
Risks of having this surgery include:
- Bulging tissue through the incision, called an incisional hernia
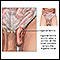
Hernia
A hernia is a sac formed by the lining of the abdominal cavity (peritoneum). The sac comes through a hole or weak area in the strong layer of the be...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Damage to nearby organs in the body
- Diarrhea
- Problems with your ileostomy
- Scar tissue that forms in your belly and causes a blockage of your intestines
-
Short bowel syndrome (when a large amount of the small intestine needs to be removed), which may lead to problems absorbing important nutrients and vitamins
Short bowel syndrome
Short bowel syndrome is a problem that occurs when part of the small intestine is missing or has been removed during surgery. Nutrients are not prop...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic anemia
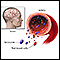
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Different type...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - The ends of your intestines that are sewn together come apart (anastomotic leak, which may be life threatening)
- Wound breaking open
- Wound infection
Before the Procedure
Talk with your surgeon or nurse about how surgery will affect:
- Intimacy and sexuality
- Pregnancy
- Sports
- Work
Tell your surgeon or nurse if:
- You are or could be pregnant.
- You are taking any medicines, including medicines, drugs, supplements, or herbs you bought without a prescription.
- You have been drinking a lot of alcohol, more than 1 or 2 drinks a day.
Planning for your surgery:
- If you have diabetes, heart disease, or other medical conditions, your surgeon may ask you to see the health care provider who treats you for these conditions.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHeart disease
Coronary heart disease is a narrowing of the blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart. Coronary heart disease (CHD) is also called co...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
If you smoke, it's important to cut back or quit. Smoking can slow healing and increase the risk for blood clots. Ask your provider for help quitting smoking.
If you smoke, it's important to cut bac...
There are many ways to quit smoking. There are also resources to help you. Family members, friends, and co-workers may be supportive. But to be su...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - If needed, prepare your home to make it easier to recover after surgery.
Prepare your home
Getting your home ready after you have been in the hospital often requires some preparation. Set up your home to make your life easier and safer when...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Ask your surgeon if you need to arrange to have someone drive you home after your surgery
- During the week before your surgery:
- You may be asked to temporarily stop taking medicines that keep your blood from clotting. These medicines are called blood thinners. This includes over-the-counter medicines and supplements such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), and vitamin E. Many prescription medicines are also blood thinners.
- Ask your surgeon which medicines you should still take on the day of your surgery.
- Let your surgeon know about any illness you may have before your surgery. This includes COVID-19, cold, flu, fever, herpes breakout, or other illness. If you do get sick, your surgery may need to be postponed.
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a respiratory illness that causes fever, coughing, and shortness of breath, but many other symptoms can occur....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCold
The common cold most often causes a runny nose, nasal congestion, and sneezing. You may also have a sore throat, cough, headache, or other symptoms....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleFlu
The flu (influenza) is a viral respiratory illness that causes fever, chills, runny nose, body aches, and cough. It spreads easily from person to pe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleFever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - You may be asked to go through a bowel preparation to clean your intestines of all stool. This may involve staying on a liquid diet for a few days and using laxatives.
On the day of your surgery:
- Follow instructions about when to stop eating and drinking.
- Take the medicines your surgeon told you to take with a small sip of water.
- Arrive at the hospital on time.
After the Procedure
You will be in the hospital for 3 to 7 days. You may have to stay longer if your surgery was an emergency operation.
You also may need to stay longer if a large amount of your small intestine was removed or you develop problems.
By the second or third day, you will most likely be able to drink clear liquids. Thicker fluids and then soft foods will be added as your bowel begins to work again.
If a large amount of your small intestine was removed, you may need to receive liquid nutrition through a vein (IV) for a period of time. A special IV will be placed in your neck or upper chest area to deliver nutrition.
After you go home, follow instructions on how to take care of yourself as you heal.
Follow instructions
You had surgery to remove all or part of your small intestine (small bowel). You may also have had an ileostomy.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most people who have a small bowel resection recover fully. Even with an ileostomy, most people are able to do the activities they were doing before their surgery. This includes most sports, travel, gardening, hiking, and other outdoor activities, and most types of work.
If a large part of your small intestine was removed, you may have problems with loose stools and getting enough nutrients from the food you eat.
If you have a long-term (chronic) condition, such as cancer, Crohn disease or ulcerative colitis, you may need ongoing medical treatment.
Crohn disease
Crohn disease is a disease where parts of the digestive tract become inflamed. It most often involves the lower end of the small intestine and the be...

Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a condition in which the lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum become inflamed. It is a form of inflammatory bowel ...
References
Albers BJ, Lamon DJ. Small bowel repair/resection. In: Baggish MS, Karram MM, eds. Atlas of Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 92.
Padilla PL, Khoo KH, Ho T, Cole EL, Sirvent RZ, Phillips LG. Small intestine. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 69.
Review Date: 1/21/2025
Reviewed By: Jonas DeMuro, MD, Diplomate of the American Board of Surgery with added Qualifications in Surgical Critical Care, Assistant Professor of Surgery, Renaissance School of Medicine, Stony Brook, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.