Breathing difficulty - lying down
Waking at night short of breath; Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea; PND; Difficulty breathing while lying down; Orthopnea; Heart failure - orthopneaBreathing difficulty while lying down is an abnormal condition in which a person has a problem breathing normally when lying flat. The head must be raised by sitting or standing to be able to breathe deeply or comfortably.
A type of breathing difficulty while lying down is paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea. This condition causes a person to wake up suddenly during the night feeling short of breath.
Considerations
This is a common complaint in people with some types of heart or lung problems. Sometimes the problem is subtle. People may only notice it when they realize that sleep is more comfortable with lots of pillows under their head, or their head in a propped-up position.
Causes
Causes may include:
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease. Having COPD makes it hard to breathe. There are two main forms of COPD:Chroni...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cor pulmonale
Cor pulmonale
Cor pulmonale is a condition that causes the right side of the heart to fail. Long-term high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries of the lung an...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Obesity (does not directly cause difficulty breathing while lying down but often worsens other conditions that lead to it)
Obesity
Obesity means weighing more than what is healthy for a given height. Obesity is a serious, chronic disease. It can lead to other health problems, i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Panic disorder
Panic disorder
Panic disorder is a type of anxiety disorder in which you have repeated attacks of intense fear that something bad will happen.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Sleep apnea
Sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a problem in which your breathing pauses during sleep. This occurs because of narrowed or blocked airways.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Snoring
Snoring
Snoring is a loud, hoarse, harsh breathing sound that occurs during sleep. Snoring is common in adults. Loud, frequent snoring can make it hard for...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Home Care
Your health care provider may recommend self-care measures. For example, weight loss may be suggested if you are obese.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If you have any unexplained difficulty in breathing while lying down, call your provider.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will perform a physical exam and ask questions about the problem.
Questions may include:
- Did this problem develop suddenly or slowly?
- Is it getting worse (progressive)?
- How bad is it?
- How many pillows do you need to help you breathe comfortably?
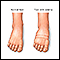
- Is there any ankle, foot, or leg swelling?
Ankle, foot, or leg swelling
Painless swelling of the feet and ankles is a common problem, especially among older people. Abnormal buildup of fluid in the ankles, feet, and legs ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Do you have difficulty breathing at other times?
- How tall are you? How much do you weigh? Has your weight changed recently?
- What other symptoms do you have?
The physical exam will include special attention to the heart and lungs (cardiovascular and respiratory systems).
Cardiovascular
The term cardiovascular refers to the heart (cardio) and the blood vessels (vascular). The cardiovascular system includes:ArteriesArteriolesCapillar...

Respiratory
The words "respiratory" and "respiration" refer to the lungs and breathing.

Tests that may be performed include the following:
-
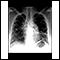
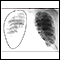
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Echocardiogram
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pulmonary function tests
Pulmonary function tests
Pulmonary function tests are a group of tests that measure breathing and how well the lungs are functioning.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment depends on the cause of the breathing problem.
You may need to use oxygen.
References
Braithwaite SA, Wessel AL. Dyspnea. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 21.
Fajardo E, Davis JL. History and physical examination. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 18.
Januzzi JL, Mann DL. Approach to the patient with heart failure. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 48.
McMurray JJV, Pfeffer MA. Heart failure: treatment and prognosis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 46.
-
Breathing - illustration
Breathing consists of two phases. The first phase is the inspiration phase. Inspiration allows air to flow into the lungs. The second phase is expiration. Expiration involves gases leaving the lungs. During inspiration, the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract allowing air to enter the lungs. During expiration, the inspiration muscles relax forcing gases to flow out of the lungs.
Breathing
illustration
-
Breathing - illustration
Breathing consists of two phases. The first phase is the inspiration phase. Inspiration allows air to flow into the lungs. The second phase is expiration. Expiration involves gases leaving the lungs. During inspiration, the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract allowing air to enter the lungs. During expiration, the inspiration muscles relax forcing gases to flow out of the lungs.
Breathing
illustration
Review Date: 1/1/2025
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor Emeritus, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


