Malaise
General ill feelingMalaise is a general feeling of discomfort, illness, or lack of well-being.
Considerations
Malaise is a symptom that can occur with almost any health condition. It may start slowly or quickly, depending on the type of disease.
Fatigue (feeling tired) occurs with malaise in many diseases. You can have a feeling of not having enough energy to do your usual activities.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.

Causes
The following lists give examples of the diseases, conditions, and medicines that can cause malaise.
SHORT-TERM (ACUTE) INFECTIOUS DISEASE
- Acute bronchitis or pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Acute viral syndrome
-
COVID-19
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a respiratory illness that causes fever, coughing, and shortness of breath, but many other symptoms can occur....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Infectious mononucleosis (EBV)
Infectious mononucleosis
Mononucleosis, or mono, is a viral infection that causes fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands, most often in the neck.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Influenza
Influenza
The flu (influenza) is a viral respiratory illness that causes fever, chills, runny nose, body aches, and cough. It spreads easily from person to pe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Lyme disease
Lyme disease
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection that is spread through the bite of one of several types of ticks.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
LONG-TERM (CHRONIC) INFECTIOUS DISEASE
-
AIDS
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic active hepatitis
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is swelling and inflammation of the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Disease caused by parasites
-
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
HEART AND LUNG (CARDIOPULMONARY) DISEASE
-
Congestive heart failure
Congestive heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease. Having COPD makes it hard to breathe. There are two main forms of COPD:Chroni...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ORGAN FAILURE
- Acute or chronic kidney disease
- Acute or chronic liver disease
Liver disease
The term "liver disease" applies to many conditions that stop the liver from working or prevent it from functioning well. Abdominal pain or swelling...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
CONNECTIVE TISSUE DISEASE
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease that leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It is a long-term disease. It can also aff...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, and other tissues.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
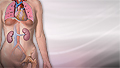
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ENDOCRINE or METABOLIC DISEASE
-
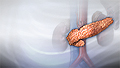
Adrenal gland dysfunction
Adrenal gland
The adrenal glands are two small triangle-shaped glands in the upper abdomen. One gland is located on top of each kidney.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Diabetes
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pituitary gland dysfunction (rare)
- Thyroid disease
CANCER
-
Leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that begins in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft tissue in the center of the bones, where blood cells are ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lymphoma (cancer that starts in the lymph system)
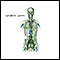
Lymph system
The lymph system is a network of organs, lymph nodes, lymph ducts, and lymph vessels that make and move lymph from tissues to the bloodstream. The l...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
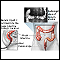
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Solid tumor cancers, such as colon cancer
Colon cancer
Colorectal cancer is cancer that starts in the large intestine (colon) or the rectum (end of the colon). It is also sometimes simply called colon ca...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
BLOOD DISORDERS
- Severe anemia
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Different type...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
PSYCHIATRIC
-
Depression
Depression
Depression is feeling sad, blue, unhappy, or down in the dumps. Most people feel this way once in a while. Major depression is a mood disorder. It...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Dysthymia
Dysthymia
Persistent depressive disorder (PDD) is a chronic (ongoing) type of depression in which a person's moods are regularly low. Persistent depressive dis...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
MEDICINES
- Anticonvulsant (antiseizure) medicines
- Antihistamines
- Beta blockers (medicines used to treat heart disease or high blood pressure)
- Psychiatric medicines
- Treatments involving several medicines
Home Care
Contact your health care provider right away if you have severe malaise.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have other symptoms with the malaise
- Malaise lasts longer than one week, with or without other symptoms
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask questions such as:
- How long has this feeling lasted (weeks or months)?
- What other symptoms do you have?
- Is the malaise constant or episodic (comes and goes)?
- Can you complete your daily activities? If not, what limits you?
- Have you traveled recently?
- What medicines are you taking?
- What are your other medical problems?
- Do you use alcohol or other drugs?
You may have tests to confirm the diagnosis if your provider thinks the problem may be due to an illness. These may include blood tests, x-rays, or other diagnostic tests.
Your provider will recommend treatment if needed based on your exam and tests.
References
Melia MT. Approach to fever or suspected infection in the normal host. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 259.
Nield LS, Kamat D. Fever. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 219.
Simel DL. History and physical examination. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 6.
-
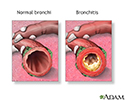
Bronchitis - illustration
Bronchitis is the inflammation of the bronchi, the main air passages to the lungs. It often results from a respiratory infection caused by a virus or bacteria. Symptoms include coughing, shortness of breath, wheezing and fatigue.
Bronchitis
illustration
Review Date: 1/1/2025
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor Emeritus, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.