Nausea and vomiting – adults
Emesis; Vomiting; Stomach upset; Upset stomach; QueasinessNausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach."
Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up through the food pipe (esophagus) and out of the mouth.
Causes
Common problems that may cause nausea and vomiting include:
-
Food allergies
Food allergies
A food allergy is a type of immune response triggered by eggs, peanuts, milk, shellfish or some other specific food.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infections of the stomach or bowels, such as the "stomach flu" or food poisoning
Food poisoning
Food poisoning occurs when you swallow food or water that contains bacteria, parasites, viruses, or the toxins made by these germs. Most cases are c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Leaking of stomach contents (food or liquid) upward (also called gastroesophageal reflux or GERD)
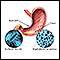
Gastroesophageal reflux
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a condition in which the stomach contents leak backward from the stomach into the esophagus (food pipe). F...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines or medical treatments, such as cancer chemotherapy or radiation treatment
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Migraine headaches
Migraine headaches
A migraine is a type of headache. It may occur with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light and sound. In most people, a throbbi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Morning sickness during pregnancy
Morning sickness
Morning sickness is nausea and vomiting that can occur at any time of the day during pregnancy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Seasickness or motion sickness
- Severe pain, such as with kidney stones
- Excessive use of marijuana
Nausea and vomiting may also be early warning signs of more serious medical problems, such as:
-
Appendicitis
Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a condition in which your appendix gets inflamed. The appendix is a small pouch attached to the end of the large intestine.
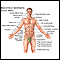 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blockage in the intestines
Blockage in the intestines
Intestinal obstruction is a partial or complete blockage of the bowel. The contents of the intestine cannot pass through it.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cancer or a tumor
- Ingesting a drug or poison, especially by children
-
Ulcers in the lining of the stomach or small intestine
Ulcers in the lining of the stomach or ...
A peptic ulcer is an open sore or raw area in the lining of the stomach (gastric ulcer) or in the first part of the small intestine (duodenal ulcer)....
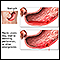 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Home Care
Once your health care provider finds the cause, you will want to know how to treat your nausea or vomiting.
How to treat your nausea or vomiting
Having nausea (being sick to your stomach) and vomiting (throwing up) can be very difficult to go through. Use the information below to help you mana...

You may need to:
- Take medicine.
- Change your diet, or try other things to make you feel better.
- Drink small amounts of clear liquids often.
Clear liquids
A clear liquid diet is made up of only clear fluids and foods that are clear fluids when they are at room temperature. This includes things such as:...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
If you have morning sickness during pregnancy, ask your provider about possible treatments.
The following may help treat motion sickness:
- Remaining still.
- Taking over-the-counter antihistamines, such as dimenhydrinate (Dramamine).
- Using prescription scopolamine skin patches (such as Transderm Scop). These are helpful for extended trips, such as an ocean voyage. Use the patch as your provider instructs. Scopolamine is for adults only. It should NOT be given to children.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call 911 or the local emergency number or go to an emergency room if you:
- Think the vomiting is from poisoning
- Notice blood or dark, coffee-colored material in the vomit
Call a provider right away or seek medical care if you or another person has:
- Been vomiting for longer than 24 hours
- Been unable to keep any fluids down for 12 hours or more
- Headache or stiff neck
- Not urinated for 8 or more hours
- Severe stomach or belly pain
- Vomited 3 or more times in 1 day
Signs of dehydration include:
Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when your body does not have as much water and fluids as it needs. Dehydration can be mild, moderate, or severe, based on how much...

- Crying without tears
- Dry mouth
- Increased thirst
- Eyes that appear sunken
- Skin changes: For example, if you touch or squeeze the skin, it doesn't bounce back the way it usually does
- Urinating less often or having dark yellow urine
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and will look for signs of dehydration.
Your provider will ask questions about your symptoms, such as:
- When did the vomiting begin? How long has it lasted? How often does it occur?
- Does it occur after you eat, or on an empty stomach?
- Are other symptoms present such as abdominal pain, fever, diarrhea, or headaches?
- Are you vomiting blood?
Vomiting blood
Vomiting blood is regurgitating (throwing up) contents of the stomach that contains blood. Vomited blood may appear bright red, dark red, or look lik...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Are you vomiting anything that looks like coffee grounds?
- Are you vomiting undigested food?
- When was the last time you urinated?
Other questions you may be asked include:
- Have you been losing weight?
- Have you been traveling? Where?
- What medicines do you take?
- Did other people who ate at the same place as you have the same symptoms?
- Are you pregnant or could you be pregnant?
- Do you use marijuana? If yes, how often do you use it?
Diagnostic tests that may be performed include:
- Blood tests (such as CBC with differential, blood electrolyte levels, and kidney and liver function tests)
CBC
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
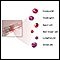 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDifferential
The blood differential test measures the percentage of each type of white blood cell (WBC) that you have in your blood. It also reveals if there are...
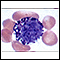 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleElectrolyte
Electrolytes are minerals in your blood and other body fluids that carry an electric charge. Electrolytes affect how your body functions in many ways...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Imaging studies (ultrasound or CT) of the abdomen
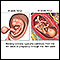
Ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCT
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Depending on the cause and how much extra fluids you need, you may have to stay in the hospital or clinic for a period of time. You may need fluids given through your veins (intravenous or IV).
References
Crane BT, Kaylie DM. Central vestibular disorders. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 168.
Guttman J. Nausea and vomiting. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 25.
McQuaid KR. Approach to the patient with gastrointestinal disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 118.
-
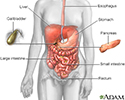
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
Review Date: 8/7/2023
Reviewed By: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.