Urination - painful
Dysuria; Painful urinationPainful urination is any pain, discomfort, or burning sensation when passing urine.
Considerations
Pain may be felt right where the urine passes out of the body. Or, it may be felt inside the body, behind the pubic bone, or in the bladder or prostate.
Pain with urination is a fairly common problem. People who have pain with urination also may have the urge to urinate more often.
Urinate more often
Frequent urination means needing to urinate more often than usual. Urgent urination is a sudden, strong need to urinate. This causes a discomfort i...

Causes
Painful urination is most often caused by an infection or inflammation somewhere in the urinary tract, such as:
-
Bladder infection (adult)
Bladder infection (adult)
A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. The infection can occur at different points in the urinary tract, including...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bladder infection (child)
Bladder infection (child)
A urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection of the urinary tract. This article discusses urinary tract infections in children. The infection ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Swelling and irritation of the tube that carries urine out of the body (urethra)
Swelling and irritation of the tube tha...
Urethritis is inflammation (swelling and irritation) of the urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the body.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Painful urination in women and girls may be due to:
- Changes in the vaginal tissue during menopause (atrophic vaginitis)
Atrophic vaginitis
Vaginal dryness is present when the tissues of the vagina are not well-lubricated and healthy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Herpes infection in the genital area
Herpes infection
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection. It is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). This article focuses on HSV type 2 infection....
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Irritation of the vaginal tissue caused by bubble bath, perfumes, or lotions
-
Vulvovaginitis, such as yeast or other infections of the vulva and vagina
Vulvovaginitis
Vulvovaginitis or vaginitis is swelling or infection of the vulva and vagina. Vaginitis is a common problem that can affect women and girls of all ag...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Other causes of painful urination include:
-
Interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a long-term (chronic) problem in which pain, pressure, or burning is present in the bladder. It is often associated wi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Prostate infection (prostatitis)
Prostatitis
Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland. This problem can be caused by an infection with bacteria. However, this is not a common cause. A...
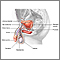 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Radiation cystitis - damage to the bladder lining from radiation therapy to the pelvis area
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as gonorrhea or chlamydia
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI).
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleChlamydia
Chlamydia is an infection caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis. It is most often spread through sexual contact.
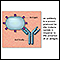 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bladder spasms
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if:
- There is drainage or a discharge from your penis or vagina.
- You are pregnant and are having any painful urination.
- You have painful urination that lasts for more than 1 day.
- You notice blood in your urine.
- You have a fever.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask questions such as:
- When did the painful urination begin?
- Does the pain occur only during urination? Does it stop after urination?
- Do you have other symptoms such as back pain?
- Have you had a fever higher than 100°F (37.7°C)?
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Is there drainage or discharge between urinations? Is there an abnormal urine odor? Is there blood in the urine?
Blood in the urine
Blood in your urine is called hematuria. The amount may be very small and only detected with urine tests or under a microscope. In other cases, the...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Are there any changes in the volume or frequency of urination?
- Do you feel the urge to urinate?
- Are there any rashes or itching in the genital area?
Rashes
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleItching
Itching is a tingling or irritation of the skin that makes you want to scratch the area. Itching may occur all over the body or only in one location...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - What medicines are you taking?
- Are you pregnant or could you be pregnant?
- Have you had a bladder infection in the past?
- Do you have any allergies to any medicines?
Allergies
An allergy is an immune response or reaction to substances that are usually not harmful.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Have you had sexual intercourse with someone who has, or may have, gonorrhea or chlamydia?
- Has there been a recent change in your brand of soap, detergent, or fabric softener?
- Have you had surgery or radiation to your urinary or sexual organs?
A urinalysis will be done. A urine culture may be ordered. If you have had a previous bladder or kidney infection, a more detailed history and physical exam are needed. Extra lab tests will also be needed. A pelvic exam and exam of vaginal fluids are needed for women and girls who have vaginal discharge. Men who have discharge from the penis may need to have a urethral swab done. However, testing a urine sample may be sufficient in some cases.
Urine culture
A urine culture is a lab test to check for bacteria or other germs in a urine sample. It can be used to check for a urinary tract infection in adults...
Other tests may include:
-
Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder
Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
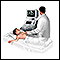 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - An exam of the inside of bladder with a lighted telescope (cystoscope)
Cystoscope
Cystoscopy is a surgical procedure. This is done to see the inside of the bladder and urethra using a thin, lighted tube.
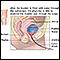 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The treatment depends on what is causing the pain.
References
Cody P. Dysuria. In: Kliegman RM, Toth H, Bordini BJ, Basel D, eds. Nelson Pediatric Symptom-Based Diagnosis. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 21.
Cooper KL, Badalato GM, Rutman MP. Infections of the urinary tract. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 55.
Germann CA. Urologic disorders. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 85.
Sobel JD, Brown P. Urinary tract infections. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 72.
-
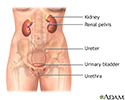
Female urinary tract - illustration
The female and male urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Female urinary tract
illustration
-
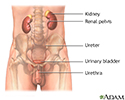
Male urinary tract - illustration
The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Male urinary tract
illustration
-
Female urinary tract - illustration
The female and male urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Female urinary tract
illustration
-
Male urinary tract - illustration
The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Male urinary tract
illustration
Review Date: 1/1/2025
Reviewed By: Kelly L. Stratton, MD, FACS, Associate Professor, Department of Urology, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.