Painful menstrual periods
Menstruation - painful; Dysmenorrhea; Periods - painful; Cramps - menstrual; Menstrual crampsPainful menstrual periods are periods in which a woman has crampy lower abdominal pain, which can be sharp or aching and come and go. Back pain and/or leg pain may also be present.
Some pain during your period is normal, but a large amount of pain is not. The medical term for painful menstrual periods is dysmenorrhea.
Considerations
Many women have painful periods. Sometimes, the pain makes it hard to do normal household, job, or school-related activities for a few days during each menstrual cycle. Painful menstruation is the leading cause of lost time from school and work among women in their teens and 20s.
Causes
Painful menstrual periods fall into two groups, depending on the cause:
- Primary dysmenorrhea
- Secondary dysmenorrhea
Primary dysmenorrhea is menstrual pain that occurs around the time that menstrual periods first begin in otherwise healthy young women. In most cases, this pain is not related to a specific problem with the uterus or other pelvic organs. Increased activity of the hormone prostaglandin, which is produced in the uterus, is thought to play a role in this condition.
Secondary dysmenorrhea is menstrual pain that develops later in women who have had normal periods. It is often related to problems in the uterus or other pelvic organs, such as:
-
Endometriosis
Endometriosis
Endometriosis occurs when cells from the lining of your womb (uterus) grow in other areas of your body. This can cause pain, heavy vaginal bleeding,...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fibroids
Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are tumors that grow in a woman's womb (uterus). These growths are typically not cancerous (benign), and do not become cancerous....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Intrauterine device (IUD) made of copper
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
-
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
Premenstrual syndrome
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) refers to a wide range of symptoms. The symptoms start during the second half of the menstrual cycle (14 or more days af...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sexually transmitted infection
- Stress and anxiety
Home Care
The following steps may help you to avoid prescription medicines:
- Apply a heating pad to your lower belly area, below your belly button. Never fall asleep with the heating pad on.
- Do light circular massage with your fingertips around your lower belly area.
- Drink warm beverages.
- Eat light, but frequent meals.
- Keep your legs raised while lying down or lie on your side with your knees bent.
- Practice relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga.
- Try over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medicine, such as ibuprofen or naproxen. Start taking it the day before your period is expected to begin and continue taking it regularly for the first few days of your period.
- Try vitamin B6, calcium, and magnesium supplements, especially if your pain is associated with PMS.
- Take warm showers or baths.
- Walk or exercise regularly, including pelvic rocking exercises.
- Lose weight if you are overweight. Get regular, aerobic exercise.
If these self-care measures do not work, your health care provider may offer you treatment such as:
- Birth control pills
- Hormone-containing IUD
- Prescription anti-inflammatory medicines
- Prescription pain relievers (including narcotics, for brief periods)
- Antidepressants
- Antibiotics
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Surgery (laparoscopy) to rule out endometriosis or other pelvic disease
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider right away if you have:
- Increased or foul-smelling vaginal discharge
- Fever and pelvic pain
- Sudden or severe pain, especially if your period is more than 1 week late and you have been sexually active.
Also contact your provider if:
- Treatments do not relieve your pain after 3 months.
- You have pain and had an IUD placed more than 3 months ago.
- You pass blood clots or have other symptoms with the pain.
- Your pain occurs at times other than menstruation, begins more than 5 days before your period, or continues after your period is over.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will examine you and ask questions about your medical history and symptoms.
Tests and procedures that may be done include:
-
Complete blood count (CBC)
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cultures to check for sexually-transmitted infections
-
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy
Pelvic laparoscopy is surgery to examine the pelvic organs. It uses a viewing tool called a laparoscope. The surgery is also used to treat certain ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pelvic ultrasound
Pelvic ultrasound
A pelvic (transabdominal) ultrasound is an imaging test. It is used to examine organs in the pelvis.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment depends on what is causing your pain.
References
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Dysmenorrhea: painful periods. FAQ046. www.acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Dysmenorrhea-Painful-Periods. Updated January 2022. Accessed April 23, 2024.
Mendiratta V, Lentz GM. Primary and secondary dysmenorrhea, premenstrual syndrome, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder: etiology, diagnosis, management. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 35.
Pattanittum P, Kunyanone N, Brown J, et al. Dietary supplements for dysmenorrhea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;3(3):CD002124. PMID: 27000311 www.pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27000311/.
-
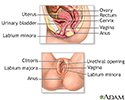
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
Relieving PMS - illustration
The cause of premenstrual syndrome is not known but severe symptoms have been shown to be responsive to lifestyle changes. Getting exercise several times a week, eating a balanced diet, getting adequate sleep, and reducing or eliminating caffeine and alcohol are some of the changes most often recommended.
Relieving PMS
illustration
-
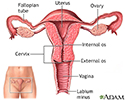
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
-
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
Relieving PMS - illustration
The cause of premenstrual syndrome is not known but severe symptoms have been shown to be responsive to lifestyle changes. Getting exercise several times a week, eating a balanced diet, getting adequate sleep, and reducing or eliminating caffeine and alcohol are some of the changes most often recommended.
Relieving PMS
illustration
-
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
Review Date: 4/16/2024
Reviewed By: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor Emeritus, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.