Foot pain
Pain - footPain or discomfort can be felt anywhere in the foot. You may have pain in the heel, toes, arch, instep, or the bottom of the foot (sole).
Heel
Heel pain is most often the result of overuse. However, it may be caused by an injury. Your heel may become tender or swollen from:Shoes with poor s...
Causes
Foot pain may be due to:
- Aging
- Being on your feet for long periods of time
- Being overweight
Overweight
Overweight and obesity mean having a weight than is higher than what is healthy for a given height. A person may be overweight from extra muscle, bo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - A foot deformity that you were born with or develops later
- Injury
- Shoes that fit poorly or do not have much cushioning
- Too much walking or other sports activity
- Trauma
The following can cause foot pain:
-
Arthritis and gout -- Common in the big toe, which becomes red, swollen, and very tender.
Arthritis
Arthritis is inflammation or degeneration of one or more joints. A joint is the area where 2 bones meet. There are more than 100 different types of...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleGout
Gout is a type of arthritis. It occurs when uric acid builds up in the blood and causes inflammation in the joints. Acute gout is a painful conditio...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Broken bones.
Broken bones
If more pressure is put on a bone than it can stand, it will split or break. A break of any size is called a fracture. If the broken bone punctures...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
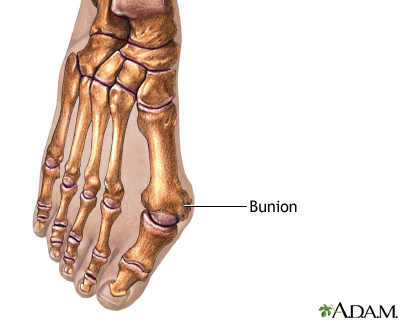
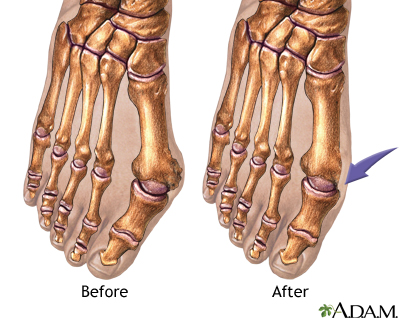
Bunions -- A bump at the base of the big toe from wearing narrow-toed shoes or from abnormal bone alignment.
Bunions
A bunion forms when your big toe points outward toward your second toe. This causes a bump to appear on the inside edge of your toe.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Calluses and corns -- Thickened skin from rubbing or pressure. Calluses are on the balls of the feet or heels. Corns appear on the top of your toes.
Calluses and corns
Corns and calluses are thick layers of skin. They are caused by repeated pressure or friction at the spot where the corn or callus develops....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hammer toes -- Toes that curl downward into a claw-like position.
Hammer toes
Hammer toe is a deformity of the toe. The toe moves into a claw-like position. The end of the toe is bent downward.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fallen arches -- Also called flat feet.
Fallen arches
Flat feet (pes planus) refer to a difference in foot shape in which the foot does not have a normal arch when standing.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Morton neuroma -- A thickening of nerve tissue between the toes.
Morton neuroma
Morton neuroma is an injury to the nerve between the toes that causes thickening and pain. It commonly affects the nerve that travels between the 3r...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nerve damage from diabetes.
-
Plantar fasciitis.
Plantar fasciitis
The plantar fascia is the thick tissue on the bottom of the foot. It connects the heel bone to the toes and creates the arch of the foot. When this...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Plantar warts -- Sores on the soles of your feet due to pressure.
-
Sprains.
Sprains
A sprain is an injury to the ligaments around a joint. Ligaments are strong, flexible fibers that hold bones together. When a ligament is stretched...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stress fracture.
- Nerve problems.
- Heel spurs or Achilles tendinitis.
- Tendon or ligament tears
Home Care
The following steps may help relieve your foot pain:
- Apply ice to reduce pain and swelling.
- Keep your painful foot elevated as much as possible.
- Reduce your activity until you feel better.
- Wear shoes that fit your feet and are right for the activity you are doing.
- Wear foot pads to prevent rubbing and irritation.
- Use an over-the-counter pain medicine, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. (Talk to your health care provider first if you have a history of ulcer or liver problems.)
Other home care steps depend on what is causing your foot pain.
The following steps can prevent foot problems and foot pain:
- Wear comfortable, properly fitting and supportive shoes, with good arch support and cushioning.
- Wear shoes with plenty of room around the ball of your foot and toes and a wide toe box.
- Avoid narrow-toed shoes and high heels.
- Wear sneakers as often as possible, especially when walking.
- Replace running shoes frequently.
- Warm up and cool down when exercising. Always stretch first.
- Stretch your Achilles tendon. A tight Achilles tendon can lead to poor foot mechanics.
- Increase your amount of exercise slowly over time to avoid putting excessive strain on your feet.
- Stretch the plantar fascia or the bottom of your feet.
- Lose weight if you need to.
- Learn exercises to strengthen your feet and avoid pain. This can help flat feet and other potential foot problems.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have sudden, severe foot pain.
- Your foot pain began following an injury, especially if your foot is bleeding or bruising, or you cannot put weight on it.
- You have redness or swelling of the joint, an open sore or ulcer on your foot, or a fever.
- You have pain in your foot and have diabetes or a disease that affects blood flow.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Your foot does not feel better after using at-home treatments for 1 to 2 weeks.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will do a physical exam. Your provider will ask questions about your symptoms and medical history.
X-rays or MRI may be done to help your provider diagnose the cause of your foot pain.
X-rays
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...

MRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
Treatment depends on the exact cause of the foot pain. Treatment may include:
- A splint or a cast, if you broke a bone
- Shoes that protect your feet
- Removal of plantar warts, corns, or calluses by a foot specialist
- Orthotics, or shoe inserts
- Physical therapy to relieve tight or overused muscles
- Foot surgery
References
Chiodo CP, Price MD, Sangeorzan AP. Foot and ankle pain. In: Firestein GS, Budd RC, Gabriel SE, Koretzky GA, McInnes IB, O'Dell JR, eds. Firestein & Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 52.
Grear BJ. Disorders of tendons and fascia and adolescent and adult pes planus. In: Azar FM, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 83.
Hickey B, Mason L, Perera A. Forefoot problems in sport. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR, eds. DeLee, Drez, & Miller's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 121.
Kadakia AR, Aiyer AA. Heel pain and plantar fasciitis: hindfoot conditions. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR, eds. DeLee, Drez, & Miller's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 120.
Rothenberg P, Swanton E, Molloy A, Aiyer AA, Kaplan JR. Ligamentous injuries of the foot and ankle. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR, eds. DeLee, Drez, & Miller's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 117.
-
Normal foot X-ray - illustration
Along with questions of your medical history, your doctor may need to take X-rays of your foot to help aid in making a diagnosis to determine the cause of your foot pain. If the foot is broken it will be put into a cast. Toes that are broken are taped.
Normal foot X-ray
illustration
-
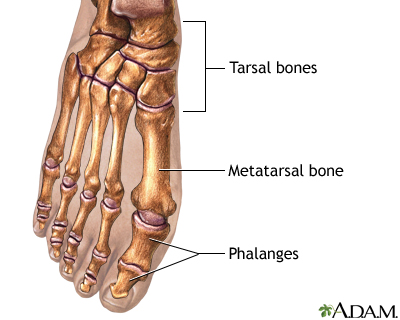
Normal toes - illustration
The foot is made up of tarsal bones, metatarsal bones and phalanges.
Normal toes
illustration
-
Proper fitting shoe - illustration
Shoes should be comfortable and fit well when you buy them. Never buy shoes that are tight, hoping they will stretch as you wear them. Because of nerve damage, people with diabetes may not feel a shoe rubbing against the skin of their foot. Blisters and sores may then develop. This can be worse if toenails are long, thick, or jagged. In people with diabetes, feet may not heal well if they get injured because of poor blood flow. This can lead to a serious infection.
Proper fitting shoe
illustration
-
Corns and calluses - illustration
Corns and calluses form on the skin because of repeated pressure or friction. A corn is a small, tender area of thickened skin that occurs on the top or side of a toe. A callus is a rough, thickened area of skin that appears because of repeated irritation or pressure to an area of skin. Calluses usually develop on the palms of the hand and soles of the feet.
Corns and calluses
illustration
-
Plantar wart - illustration
Plantar warts are found on the soles of the feet. Because of their location, they can become extremely painful. Large numbers of plantar warts on the foot may cause difficulty when running and even walking.
Plantar wart
illustration
-
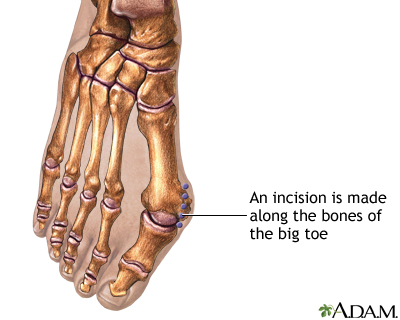
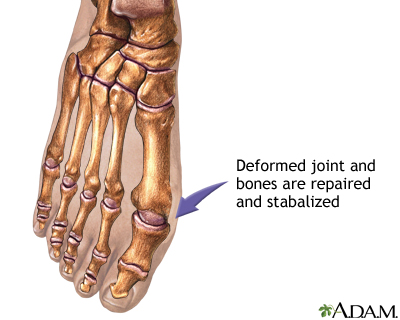
Bunion removal - Series
Presentation
-
Normal foot X-ray - illustration
Along with questions of your medical history, your doctor may need to take X-rays of your foot to help aid in making a diagnosis to determine the cause of your foot pain. If the foot is broken it will be put into a cast. Toes that are broken are taped.
Normal foot X-ray
illustration
-
Normal toes - illustration
The foot is made up of tarsal bones, metatarsal bones and phalanges.
Normal toes
illustration
-
Proper fitting shoe - illustration
Shoes should be comfortable and fit well when you buy them. Never buy shoes that are tight, hoping they will stretch as you wear them. Because of nerve damage, people with diabetes may not feel a shoe rubbing against the skin of their foot. Blisters and sores may then develop. This can be worse if toenails are long, thick, or jagged. In people with diabetes, feet may not heal well if they get injured because of poor blood flow. This can lead to a serious infection.
Proper fitting shoe
illustration
-
Corns and calluses - illustration
Corns and calluses form on the skin because of repeated pressure or friction. A corn is a small, tender area of thickened skin that occurs on the top or side of a toe. A callus is a rough, thickened area of skin that appears because of repeated irritation or pressure to an area of skin. Calluses usually develop on the palms of the hand and soles of the feet.
Corns and calluses
illustration
-
Plantar wart - illustration
Plantar warts are found on the soles of the feet. Because of their location, they can become extremely painful. Large numbers of plantar warts on the foot may cause difficulty when running and even walking.
Plantar wart
illustration
-
Bunion removal - Series
Presentation
Review Date: 6/17/2024
Reviewed By: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.