Opisthotonos
Back arching; Abnormal posturing - opisthotonos; Decerebrate posture - opisthotonosOpisthotonos is a condition in which a person holds their body in an abnormal position. The person is usually rigid and arches their back, with their head thrown backward. If a person with opisthotonos lies on their back, only the back of their head and heels touch the surface they are on.
Considerations
Opisthotonos is much more common in infants and children than in adults. It is also more extreme in infants and children because of their less mature nervous systems.
Causes
Opisthotonos may occur in infants with meningitis. This is an infection of the meninges, the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. Viruses, malaria, and syphilis are infections associated with opisthotonos. It may also occur as a sign of reduced brain function or injury to the nervous system.
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.

Malaria
Malaria is a parasitic disease that involves high fevers, shaking chills, flu-like symptoms, and anemia.
Other causes may include:
- Arnold-Chiari syndrome, a problem with the structure of the brain
-
Brain tumor
Brain tumor
A brain tumor is a group (mass) of abnormal cells that grow in the brain. This article focuses on primary brain tumors in children.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that involve the brain. This affects nervous system functions, such as movement, learning, hearing, seei...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Gaucher disease, which causes a buildup of fatty tissue in certain organs
Gaucher disease
Gaucher disease is a rare genetic disorder in which a person lacks an enzyme called glucocerebrosidase (GBA).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Growth hormone deficiency (occasionally)
Growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency means the pituitary gland does not make enough growth hormone.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Poisoning including strychnine, some street drugs, and some medicines
- Metabolic disorders that run in families, such as glutaric aciduria and organic acidemias, Krabbe disease, maple syrup urine disease, and others
Krabbe disease
Krabbe disease is a rare genetic disorder of the nervous system. It is a type of brain disease called leukodystrophy.
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleMaple syrup urine disease
Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) is a disorder in which the body cannot break down certain parts of proteins. The urine of people with this conditio...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Severe electrolyte imbalance
Electrolyte
Electrolytes are minerals in your blood and other body fluids that carry an electric charge. Electrolytes affect how your body functions in many ways...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) can occur when the head hits an object, or a moving object strikes the head. There are three types of TBI:Mild TBI, a...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stiff-person syndrome (a condition that makes a person rigid and have spasms)
- Bleeding in the brain
-
Tetanus
Tetanus
Tetanus is an infection of the nervous system with a type of bacteria that is potentially deadly, called Clostridium tetani (C tetani).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Some antipsychotic medicines can cause a side effect called acute dystonic reaction. Opisthotonos may be part of this reaction.
Acute
Acute means sudden. Acute symptoms appear, change, or worsen rapidly. It is the opposite of chronic.
In rare cases, infants born to women who drink large amounts of alcohol during pregnancy may have opisthotonos due to alcohol withdrawal.
Home Care
A person who develops opisthotonos will need to be checked at a hospital and may need to be admitted to a hospital for care.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Go to the emergency room or call 911 or the local emergency number if symptoms of opisthotonos occur. Typically, opisthotonos is a symptom of other conditions that are serious enough for a person to seek medical attention.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
This condition will be evaluated in a hospital, and emergency measures may be taken.
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about symptoms to look for the cause of opisthotonos
Physical exam
During a physical examination, a health care provider checks your body to determine if you do or do not have a physical problem. A physical examinati...
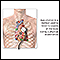
Questions may include:
- When did the symptoms start?
- Is the body positioning always the same?
- What other symptoms came before or with the abnormal positioning (such as fever, stiff neck, or headache)?
Abnormal positioning
Decerebrate posture is an abnormal body posture that involves the arms and legs being held straight out, the toes being pointed downward, and the hea...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Is there any recent history of illness?
The physical exam will include a complete checkup of the nervous system.
Tests may include:
- Blood and urine tests
-
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) culture and cell counts
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) culture
A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) culture is a lab test to look for bacteria, fungi, and viruses in the fluid that moves in the space around the spinal cor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCell counts
A CSF cell count is a test to measure the number of red and white blood cells that are in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is a clear fluid that is in...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan of the head
CT scan of the head
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Electrolyte analysis
Electrolyte
Electrolytes are minerals in your blood and other body fluids that carry an electric charge. Electrolytes affect how your body functions in many ways...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
MRI of the brain
MRI of the brain
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment will depend on the cause. For example, if meningitis is the cause, medicines may be given.
References
Berger JR, Price R. Stupor and coma. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 5.
Birch TB, Bleck TP. Tetanus (Clostridium tetani). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 244.
Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al. Defects in metabolism of amino acids. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 105.
-
Meninges of the brain - illustration
The organs of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) are covered by connective tissue layers collectively called the meninges. Consisting of the pia mater (closest to the CNS structures), the arachnoid and the dura mater (farthest from the CNS), the meninges also support blood vessels and contain cerebrospinal fluid. These are the structures involved in meningitis, an inflammation of the meninges, which, if severe, may become encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain.
Meninges of the brain
illustration
-
Meninges of the brain - illustration
The organs of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) are covered by connective tissue layers collectively called the meninges. Consisting of the pia mater (closest to the CNS structures), the arachnoid and the dura mater (farthest from the CNS), the meninges also support blood vessels and contain cerebrospinal fluid. These are the structures involved in meningitis, an inflammation of the meninges, which, if severe, may become encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain.
Meninges of the brain
illustration
Review Date: 4/16/2025
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


