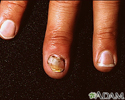
Nail abnormalities
Beau lines; Fingernail abnormalities; Spoon nails; Onycholysis; Leukonychia; Koilonychia; Brittle nailsNail abnormalities are problems with the color, shape, texture, or thickness of the fingernails or toenails.
Considerations
Like the skin, the fingernails tell a lot about your health:
- Beau lines (also called Beau's lines) are depressions across the fingernail. These lines can occur after illness, injury to the nail, eczema around the nail, during chemotherapy for cancer, or when you do not get enough nutrition.
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Brittle nails are often a normal result of aging. They can also be due to certain diseases and conditions.
- Koilonychia is an abnormal shape of the fingernail. The nail has raised ridges and is thin and curved inward. This disorder is associated with iron deficiency anemia.
Iron deficiency anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. There are man...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Leukonychia is white streaks or spots on the nails often due to medicines or disease.
- Pitting is the presence of small depressions on the nail surface. Sometimes the nail is also crumbling. The nail can become loose and sometimes falls off. Pitting is associated with psoriasis and alopecia areata.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin condition that causes skin redness, silvery scales, and irritation. Most people with psoriasis have thick, red, well-defined pat...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAlopecia areata
Alopecia areata is a condition that causes round patches of hair loss. It can lead to total hair loss.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ridges are tiny, raised lines that develop across or up and down the nail.
Causes
Injury:
- Crushing the base of the nail or the nail bed may cause a permanent deformity.
- Chronic picking or rubbing of the skin behind the nail can cause median nail dystrophy, which gives a lengthwise split or ridged appearance of the thumbnails.
- Long-term exposure to moisture or nail polish can cause nails to peel and become brittle.
Infection:
- Fungus or yeast cause changes in the color, texture, and shape of the nails.
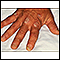
- Bacterial infection may cause a change in nail color or painful areas of infection under the nail or in the surrounding skin. Severe infections may cause nail loss. Paronychia is an infection around the nailfold and cuticle.
Paronychia
Paronychia is a skin infection that occurs around the nails.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Viral warts may cause a change in the shape of the nail or ingrown skin under the nail.
Warts
Warts are small, usually painless growths on the skin. Most of the time, they are harmless. They are caused by a virus called human papillomavirus ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Certain infections (especially of the heart valve) may cause red streaks in the nail bed (splinter hemorrhages).
Splinter hemorrhages
Splinter hemorrhages are small areas of bleeding (hemorrhage) under the fingernails or toenails.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Diseases:
- Disorders that affect the amount of oxygen in the blood (such as heart problems and lung diseases including cancer or infection) may cause clubbing.
Clubbing
Clubbing is changes in the areas under and around the toenails and fingernails that occur with some disorders. The nails may also show changes....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney disease can cause a build-up of nitrogen waste products in the blood, which can damage nails.
-
Liver disease can damage nails.
Liver disease
The term "liver disease" applies to many conditions that stop the liver from working or prevent it from functioning well. Abdominal pain or swelling...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Thyroid diseases such as hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism may cause brittle nails or splitting of the nail bed from the nail plate (onycholysis).
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. The condition is often called overactive thyroid.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. This condition is often called underactive thyroid....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Severe illness or surgery may cause horizontal depressions in the nails called Beau lines.
-
Psoriasis may cause pitting, splitting of the nail plate from the nail bed, and chronic (long-term) destruction of the nail plate (nail dystrophy).
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin condition that causes skin redness, silvery scales, and irritation. Most people with psoriasis have thick, red, well-defined pat...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Other conditions that can affect the appearance of the nails include systemic amyloidosis, malnutrition, vitamin deficiency, and lichen planus.
Amyloidosis
Primary amyloidosis is a rare disorder in which abnormal proteins build up in tissues and organs. Clumps of the abnormal proteins are called amyloid...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleLichen planus
Lichen planus is a condition that forms a very itchy rash on the skin or in the mouth.
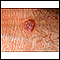 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Skin cancers near the nail and fingertip can distort the nail. Subungual melanoma is a potentially deadly cancer that will normally appear as a dark streak down the length of the nail.
- Hutchinson sign is a darkening of the cuticle associated with a pigmented streak and may be a sign of an aggressive melanoma.
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer. It is also the rarest. It is the leading cause of death from skin disease. Other common types o...
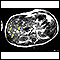 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Poisons:
- Arsenic poisoning may cause white lines and horizontal ridges.
- Silver intake can cause a blue nail.
Medicines:
- Certain antibiotics can cause lifting of the nail from the nail bed.
-
Chemotherapy medicines can affect nail growth.
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Normal aging affects the growth and development of the nails.
Home Care
To prevent nail problems:
- Do not bite, pick, or tear at your nails (in severe cases, some people may need counseling or encouragement to stop these behaviors).
- Keep hangnails clipped.
- Wear shoes that do not squeeze the toes together, and always cut toenails straight across along the top.
- To prevent brittle nails, keep the nails short and do not use nail polish. Use an emollient (skin softening) cream after washing or bathing.
Bring your own manicure tools to nail salons and do not allow the manicurist to work on your cuticles.
Using the vitamin biotin in high doses [5,000 micrograms (mg) daily] and clear nail polish that contains protein can help strengthen your nails. Ask your health care provider about medicines that help with abnormal-appearing nails. If you have a nail infection, you may be prescribed antifungal or antibacterial medicines.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have:
- Blue nails
- Clubbed nails
- Distorted nails
- Horizontal ridges
- Pale nails
- White lines
- White color under the nails
- Pits in your nails
- Peeling nails
- Painful nails
- Ingrown nails
If you have splinter hemorrhages or Hutchinson sign, contact your provider immediately.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will look at your nails and ask about your symptoms. Questions may include whether you injured your nail, if your nails are constantly exposed to moisture, or whether you are always picking at your nails.
Tests that may be ordered include x-rays, blood tests, or examination of parts of the nail or the nail matrix in the lab.
References
American Academy of Dermatology website. 12 nail changes a dermatologist should examine. www.aad.org/public/everyday-care/nail-care-secrets/basics/nail-changes-dermatologist-should-examine. Accessed June 12, 2025.
Tosti A. Diseases of hair and nails. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 409.
Tosti A, Piraccini BM. Nail disorders. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 71.
-
Nail infection - candidal - illustration
A paronychia is an infection around the nail. Many organisms can cause a paronychia. This particular case is caused by the yeast-like organism Candida. Note the inflammation (red, swollen area) at the base of the nail and the changes that are apparent in the nail itself.
Nail infection - candidal
illustration
-
Koilonychia - illustration
Nails may exhibit many different abnormalities. In the condition known as koilonychia, the nails are flattened and have concavities. This condition may be associated with iron deficiency.
Koilonychia
illustration
-
Onycholysis - illustration
In onycholysis the nails become loose. They may even detach from the nail bed. When not held firmly in place, the nails are rapidly damaged and debris collects beneath them.
Onycholysis
illustration
-
White nail syndrome - illustration
White nail syndrome may also be called leukonychia. Leukonychia can occur with arsenic poisoning, heart disease, renal failure, pneumonia, or hypoalbuminemia.
White nail syndrome
illustration
-
Yellow nail syndrome - illustration
Yellow nail syndrome is characterized by yellow nails that lack a cuticle, grow slowly, and are loose or detached (onycholysis). Yellow nail syndrome is most commonly associated with lung disorders, and with lymphedema.
Yellow nail syndrome
illustration
-
Half and half nails - illustration
Internal diseases and nutritional deficits can cause changes in the appearance of the nails.
Half and half nails
illustration
-
Yellow nails - illustration
Yellow nails are seen in the 'yellow nail syndrome' in which there is thickening and yellow to yellow-green discoloration of all nails. Lymphedema, especially of the ankles, and compromised respiration may be present. The nails may also be over-curved both transversely and longitudinally. Lunulae and cuticles may also be lost.
Yellow nails
illustration
-
Brittle nails - illustration
Like the skin, the fingernails are a reflection of a person's state of health. Low levels of zinc and iron as well as thyroid problems can cause brittle nails. However, brittle nails are often a normal result of aging.
Brittle nails
illustration
-
Nail infection - candidal - illustration
A paronychia is an infection around the nail. Many organisms can cause a paronychia. This particular case is caused by the yeast-like organism Candida. Note the inflammation (red, swollen area) at the base of the nail and the changes that are apparent in the nail itself.
Nail infection - candidal
illustration
-
Koilonychia - illustration
Nails may exhibit many different abnormalities. In the condition known as koilonychia, the nails are flattened and have concavities. This condition may be associated with iron deficiency.
Koilonychia
illustration
-
Onycholysis - illustration
In onycholysis the nails become loose. They may even detach from the nail bed. When not held firmly in place, the nails are rapidly damaged and debris collects beneath them.
Onycholysis
illustration
-
White nail syndrome - illustration
White nail syndrome may also be called leukonychia. Leukonychia can occur with arsenic poisoning, heart disease, renal failure, pneumonia, or hypoalbuminemia.
White nail syndrome
illustration
-
Yellow nail syndrome - illustration
Yellow nail syndrome is characterized by yellow nails that lack a cuticle, grow slowly, and are loose or detached (onycholysis). Yellow nail syndrome is most commonly associated with lung disorders, and with lymphedema.
Yellow nail syndrome
illustration
-
Half and half nails - illustration
Internal diseases and nutritional deficits can cause changes in the appearance of the nails.
Half and half nails
illustration
-
Yellow nails - illustration
Yellow nails are seen in the 'yellow nail syndrome' in which there is thickening and yellow to yellow-green discoloration of all nails. Lymphedema, especially of the ankles, and compromised respiration may be present. The nails may also be over-curved both transversely and longitudinally. Lunulae and cuticles may also be lost.
Yellow nails
illustration
-
Brittle nails - illustration
Like the skin, the fingernails are a reflection of a person's state of health. Low levels of zinc and iron as well as thyroid problems can cause brittle nails. However, brittle nails are often a normal result of aging.
Brittle nails
illustration
Review Date: 6/3/2025
Reviewed By: Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.