Indigestion
Dyspepsia; Uncomfortable fullness after mealsIndigestion (dyspepsia) is a mild discomfort in the upper belly or abdomen. It often occurs during or right after eating. It may feel like:
- Heat, burning, or pain in the area between the navel and the lower part of the breastbone
- Unpleasant fullness that starts soon after a meal begins or when the meal is over
Bloating and nausea are less common symptoms.
Bloating
Abdominal bloating is a condition in which the belly (abdomen) feels full and tight. Your belly may look swollen (distended).
Nausea
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...

Indigestion is NOT the same as heartburn.
Heartburn
Heartburn is a painful burning feeling just below or behind the breastbone. Most of the time, it comes from the esophagus. The pain often rises in ...

Causes
Most of the time, indigestion is not a sign of a serious health problem unless it occurs with other symptoms. These may include:
- Bleeding
- Trouble swallowing
- Weight loss
- Recurrent nausea and vomiting
Rarely, the discomfort of a heart attack is mistaken for indigestion.
Indigestion may be triggered by:
- Drinking too many caffeinated beverages
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Eating spicy, fatty, or greasy foods
- Eating too much (overeating)
- Eating too fast
- Eating high-fiber foods
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
- Stress or being nervous
Other causes of indigestion are:
-
Gallstones
Gallstones
Gallstones are hard deposits that form inside the gallbladder. These may be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Gastritis (when the lining of the stomach becomes inflamed or swollen)
Gastritis
Gastritis occurs when the lining of the stomach becomes inflamed or swollen. Gastritis may last for only a short time (acute gastritis) or it may lin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Esophagitis (inflamed esophagus)
- Swelling of the pancreas (pancreatitis)
-
Ulcers (stomach or intestinal ulcer)
Ulcers
An ulcer is a crater-like sore on the skin or mucous membrane. Ulcers form when the top layers of skin or tissue have been removed. They can occur ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Use of certain medicines such as antibiotics, aspirin, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen)
Home Care
Changing the way you eat may help your symptoms. Steps you can take include:
- Allow enough time for meals.
- Avoid arguments during meals.
- Avoid excitement or exercise right after a meal.
- Chew food carefully and completely.
- Relax and get rest if indigestion is caused by stress.
Avoid aspirin and other NSAIDs. If you must take them, do so on a full stomach.
Avoid alcohol and smoking.
Antacids may relieve indigestion.
Medicines you can buy without a prescription, such as famotidine (Zantac 360 or Pepcid AC) and omeprazole (Prilosec OTC) can relieve symptoms. There are other choices as well. In addition, your health care provider may also prescribe these or similar medicines in higher doses or for longer periods of time.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Get medical help right away if your symptoms include jaw pain, chest pain, back pain, heavy sweating, anxiety, or a feeling of impending doom. These are possible heart attack symptoms.
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.

Heavy sweating
Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition in which a person sweats excessively and unpredictably. People with hyperhidrosis may sweat even when the tempe...
Contact your provider if:
- Your indigestion symptoms change noticeably.
- Your symptoms last longer than a few days.
- You have unexplained weight loss.
Unexplained weight loss
Unexplained weight loss is a decrease in body weight, when you did not try to lose the weight on your own. Many people gain and lose weight. Uninten...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - You have sudden, severe abdominal pain.
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - You have trouble swallowing.
Trouble swallowing
The tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach is the esophagus or food pipe. Achalasia makes it harder for the esophagus to move food int...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - You have yellow coloring of the skin and eyes (jaundice).
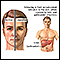
Jaundice
Jaundice is a yellow color of the skin, mucus membranes, or eyes. The yellow coloring comes from bilirubin, a byproduct of old red blood cells. Jau...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - You vomit blood or pass blood in the stool (which may appear black).
Vomit blood
Vomiting blood is regurgitating (throwing up) contents of the stomach that contains blood. Vomited blood may appear bright red, dark red, or look lik...
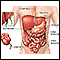
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleBlood in the stool
Black or tarry stools with a foul smell are a sign of a problem in the upper digestive tract. It most often indicates that there is bleeding in the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will do a physical exam of the stomach area and digestive tract. You will be asked questions about your symptoms.
You may have some tests, including:
- Blood tests
-
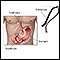
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD or upper endoscopy)
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine (the duodenum)....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
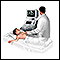
Ultrasound test of the abdomen
Ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Chang L. Irritable bowel and functional upper gastrointestinal syndromes. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 123.
Falk GW, Katzka DA. Diseases of the esophagus. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 124.
Tack J. Dyspepsia. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 14.
-
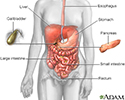
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
Review Date: 1/30/2025
Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Gastroenterologist, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.