Point tenderness - abdomen
Abdominal tendernessAbdominal point tenderness is the localized pain you feel when pressure is placed over a certain part of the belly area (abdomen).
Considerations
The abdomen is an area of the body a health care provider can easily examine by touch. The provider can feel growths and organs in the belly area and find where you feel pain.
Abdominal tenderness can be mild to severe. Rebound tenderness means that there is more pain when pressure on the tender area is released. It occurs when the tissue that lines the abdominal cavity (the peritoneum) is irritated, inflamed, or infected. This is called peritonitis.
Peritonitis
Peritonitis is an inflammation (irritation) of the peritoneum. This is the thin tissue that lines the inner wall of the abdomen and covers most of t...

Causes
Causes include:
-
Abdominal abscess
Abdominal abscess
The peritoneum is the thin tissue that lines the inner wall of the abdomen and covers most of the organs in the abdomen. Peritonitis is present when...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Appendicitis
Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a condition in which your appendix gets inflamed. The appendix is a small pouch attached to the end of the large intestine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Certain types of hernias
Hernias
A hernia is a sac formed by the lining of the abdominal cavity (peritoneum). The sac comes through a hole or weak area in the strong layer of the be...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Meckel diverticulum
Meckel diverticulum
A Meckel diverticulum is a pouch on the wall of the lower part of the small intestine that is present at birth (congenital). The diverticulum may co...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ovarian torsion (twisted fallopian tube)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Get emergency medical help right away if you have abdominal point tenderness.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will examine you and gently push on places on your belly. People with peritonitis will often tense the abdominal muscles when the area is touched. This is called guarding.
The provider will note any point of tenderness. The location of the tenderness can indicate the problem that is causing it. For example, if you have appendicitis, you will likely have tenderness when a certain place in the lower right abdomen is touched. This spot is called McBurney point.
The provider will also ask questions about your symptoms and medical history. These may include:
- When did the symptoms start?
- Is this the first time you have had such discomfort?
- If not, when does the discomfort tend to occur?
- Are you having other symptoms, such as constipation, diarrhea, fainting, vomiting, or fever?
Constipation
Constipation in infants and children means they have hard stools or have problems passing stools. A child may have pain while passing stools or may ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleVomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
You may need to have the following tests:
-
Abdominal x-ray
Abdominal x-ray
An abdominal x-ray is an imaging test to look at organs and structures in the abdomen. Organs include the liver, spleen, stomach, and intestines. T...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Abdominal CT scan (occasionally)
Abdominal CT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Abdominal ultrasound
- Blood tests, such as a complete blood count
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
In some cases, you may need surgery right away. This may involve an exploratory laparotomy or an emergency appendectomy.
Exploratory laparotomy
Abdominal exploration is surgery to look at the organs and structures in your belly area (abdomen). This includes your:AppendixBladderGallbladderIn...

Appendectomy
An appendectomy is surgery to remove the appendix.

References
Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW. Abdomen. In: Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW, eds. Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination. 10th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 18.
Landmann A, Bonds M, Postier R. Acute abdomen. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 46.
McQuaid KR. Approach to the patient with gastrointestinal disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 118.
-
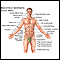
Anatomical landmarks adult - front - illustration
There are three body views (front, back, and side) that can help you to identify a specific body area. The labels show areas of the body which are identified either by anatomical or by common names. For example, the back of the knee is called the “popliteal fossa,” while the “flank” is an area on the side of the body.
Anatomical landmarks adult - front
illustration
-
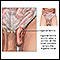
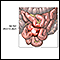
Appendix - illustration
The appendix is near the junction of the small bowel and the colon. On occasion, it may become infected. Although most people are familiar with appendicitis, it is a relatively rare disease. It is treated by surgical removal of the appendix (appendectomy). Recovery time for uncomplicated appendicitis is usually just three days.
Appendix
illustration
-
Anatomical landmarks adult - front - illustration
There are three body views (front, back, and side) that can help you to identify a specific body area. The labels show areas of the body which are identified either by anatomical or by common names. For example, the back of the knee is called the “popliteal fossa,” while the “flank” is an area on the side of the body.
Anatomical landmarks adult - front
illustration
-
Appendix - illustration
The appendix is near the junction of the small bowel and the colon. On occasion, it may become infected. Although most people are familiar with appendicitis, it is a relatively rare disease. It is treated by surgical removal of the appendix (appendectomy). Recovery time for uncomplicated appendicitis is usually just three days.
Appendix
illustration
Review Date: 10/9/2024
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.