Muscle twitching
Muscle fasciculation; Fasciculations of muscleMuscle twitches are fine movements of a small area of muscle.
Considerations
Muscle twitching is caused by minor muscle contractions in the area, or uncontrollable twitching of a muscle group that is served by a single motor nerve fiber.
Muscle contractions
Muscle cramps are when a muscle gets tight (contracts) without you trying to tighten it, and it does not relax. Cramps may involve all or part of on...

Muscle twitches are minor and often go unnoticed. Some are common and normal. Others are signs of a nervous system disorder.
Causes
Causes may include:
-
Autoimmune disorders, such as Isaac syndrome.
Autoimmune disorders
An autoimmune disease occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune di...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Drug overdose (caffeine, amphetamines, or other stimulants).
- Lack of sleep.
- Medicine side effect (such as from diuretics, corticosteroids, or estrogens).
- Exercise (twitching is seen after exercise).
- Lack of nutrients in the diet (deficiency).
- Stress.
- Medical conditions that cause metabolic disorders, including low potassium, kidney disease, and uremia.
- Twitches not caused by disease or disorders (benign twitches), often affecting the eyelids, calf, or thumb. These twitches are normal and quite common, and are often triggered by stress or anxiety. These twitches can come and go, and usually do not last for more than a few days.
Anxiety
Stress is a feeling of emotional or physical tension. It can come from any event or thought that makes you feel frustrated, angry, or nervous. Stres...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Nervous system conditions that can cause muscle twitching include:
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also sometimes called Lou Gehrig disease or motor neuron disease
ALS
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, is a disease of the nerve cells in the brain, brain stem and spinal cord that control voluntary muscle movemen...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Neuropathy or damage to the nerve that leads to a muscle
-
Spinal muscular atrophy
Spinal muscular atrophy
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a group of disorders of the motor neurons (motor cells). These disorders are passed down through families (inherite...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weak muscles (myopathy)
Symptoms of a nervous system disorder include:
- Loss of, or change in, sensation
- Loss of muscle size (wasting)
- Weakness
Home Care
No treatment is needed for benign muscle twitching in most cases. In other cases, treating an underlying medical cause may improve symptoms.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have long-term or persistent muscle twitches or if twitching occurs with weakness or loss of muscle.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will take a medical history and perform a physical exam.
Medical history questions may include:
- When did you first notice the twitching?
- How long does it last?
- How often do you experience twitching?
- What muscles are affected?
- Is it always in the same location?
- Are you pregnant?
- Are there cramps with the twitching?
- What other symptoms do you have?
Tests depend on the suspected cause, and may include:
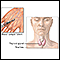
- Blood tests to look for problems with electrolytes, thyroid gland function, and blood chemistry
Electrolytes
Electrolytes are minerals in your blood and other body fluids that carry an electric charge. Electrolytes affect how your body functions in many ways...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleThyroid gland function
Thyroid function tests are used to check whether your thyroid is working normally. The most common thyroid function tests are:Free T4 (free thyroxine...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan of the spine or brain
CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
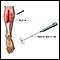
Electromyogram (EMG)
Electromyogram
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nerve conduction studies
-
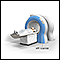
MRI scan of the spine or brain
MRI scan
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
De Luca GC, Griggs RC, Johnston SC. Approach to the patient with neurologic disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 366.
Hall JE, Hall ME. Contraction of skeletal muscle. In: Hall JE, Hall ME, eds. Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 6.
Weissenborn K, Lockwood AH. Toxic and metabolic encephalopathies. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 84.
-
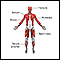
Deep anterior muscles - illustration
Muscle tissue is composed primarily of contractile cells. Contractile cells have the ability to produce movement.
Deep anterior muscles
illustration
-
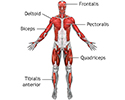
Superficial anterior muscles - illustration
Superficial muscles are close to the surface of the skin. Muscles which lie closer to bone or internal organs are called deep muscles.
Superficial anterior muscles
illustration
-
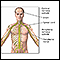
Tendons and muscles - illustration
Tendons connect muscles to their bony origins and insertions.
Tendons and muscles
illustration
-
Lower leg muscles - illustration
The muscular components of the lower leg include the gastrocnemius, soleus, peroneus longus, tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, and the Achilles tendon.
Lower leg muscles
illustration
-
Deep anterior muscles - illustration
Muscle tissue is composed primarily of contractile cells. Contractile cells have the ability to produce movement.
Deep anterior muscles
illustration
-
Superficial anterior muscles - illustration
Superficial muscles are close to the surface of the skin. Muscles which lie closer to bone or internal organs are called deep muscles.
Superficial anterior muscles
illustration
-
Tendons and muscles - illustration
Tendons connect muscles to their bony origins and insertions.
Tendons and muscles
illustration
-
Lower leg muscles - illustration
The muscular components of the lower leg include the gastrocnemius, soleus, peroneus longus, tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, and the Achilles tendon.
Lower leg muscles
illustration
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.