Spasticity
Muscle stiffness; HypertoniaSpasticity is stiff or rigid muscles. It may also be called unusual tightness or increased muscle tone. Reflexes (for example, a knee-jerk reflex) are stronger or exaggerated. The condition can interfere with walking, movement, speech, and many other activities of daily living.
Considerations
Spasticity is often caused by damage to the part of the brain that is involved in movements under your control. It may also occur from damage to the nerves in the spinal cord.
Symptoms of spasticity include:
- Abnormal posture
- Limited, slow movements
- Carrying the shoulder, arm, wrist, and finger at an abnormal angle because of muscle tightness
- Exaggerated deep tendon reflexes (the knee-jerk or other reflexes)
- Repetitive jerky motions (clonus), especially when you are touched or moved
- Scissoring (crossing of the legs as the tips of scissors would close)
- Pain or deformity of the affected area of the body
Spasticity may also affect speech. Severe, long-term spasticity may lead to contracture of muscles. This can reduce range of motion or leave the joints bent.
Contracture
A contracture develops when normally stretchy (elastic) tissues are replaced by nonstretchy (inelastic) fiber-like tissue. This tissue makes it hard...

Causes
Spasticity may be caused by any of the following:
- Brain damage caused by lack of oxygen, as can occur in near drowning or near suffocation
Near drowning
Non-fatal drowning means a person developed trouble breathing from being underwater or having their head underwater, and survived. If a person has be...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cerebral palsy (a group of disorders due to brain injury at birth)
Cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that involve the brain. This affects nervous system functions, such as movement, learning, hearing, seei...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cervical spinal stenosis
- Head injury
- Infections of brain or spinal cord (Lyme disease, syphilis, HIV, tuberculosis)
-
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease that affects the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Neurodegenerative illness (illnesses that damage the brain and nervous system over time)
-
Phenylketonuria (a disorder in which the body can't break down the amino acid phenylalanine)
Phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a rare condition in which a baby is born without the ability to properly break down an amino acid called phenylalanine....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Spinal cord injury
-
Stroke
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tumors in brain or spinal cord
- Toxins (for example, nitrous oxide or laughing gas)
- Vitamin or mineral deficiency (vitamin B12, vitamin E, copper)
This list does not include all conditions that can cause spasticity.
Home Care
Exercise, including muscle stretching, can help make symptoms less severe. Physical therapy is also helpful.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if:
- The spasticity gets worse
- You notice deformity of the affected areas
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms, including:
- When was it first noticed?
- How long has it lasted?
- Is it always present?
- How severe is it?
- Which muscles are affected?
- What makes it better?
- What makes it worse?
- What other symptoms are present?
After determining the cause of your spasticity, your provider may refer you to a physical therapist. Physical therapy involves different exercises, including muscle stretching and strengthening exercises. Physical therapy exercises can be taught to parents who can then help their child do them at home.
Other treatments may include:
- Medicines to treat spasticity. These need to be taken as instructed.
- Botulinum toxin that can be injected into the spastic muscles.
- A pump used to directly deliver medicine into the spinal fluid and nervous system, in rare cases.
- Surgery to release the tendon or to cut the nerve-muscle pathway is sometimes used.
References
De Luca GC, Griggs RC. Johnston SC. Approach to the patient with neurologic disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 366.
Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Newman NJ, Pomeroy SL. Diagnosis of neurological disease. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 1.
McGee S. Examination of the motor system: approach to weakness. In: McGee S, ed. Evidence-Based Physical Diagnosis. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 61.
Oleszek JC, Davidson LT. Spasticity. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 752.
-
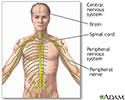
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
Review Date: 2/11/2025
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.