Hypotonia
Decreased muscle tone; Floppy infantHypotonia means decreased muscle tone.
Considerations
Hypotonia is often a sign of a worrisome problem. The condition can affect children or adults.
Infants with this problem seem floppy and feel like a "rag doll" when held. They rest with their elbows and knees loosely extended. Infants with normal tone tend to have flexed elbows and knees. They may have poor head control. The head may fall to the side, backward, or forward.
Infants with normal tone can be lifted with the adult's hands placed under the armpits. Hypotonic infants tend to slip between the hands.
Causes
Muscle tone and movement involve the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and muscles. Hypotonia may be a sign of a problem anywhere along the pathway that controls muscle movement. Causes may include:
- Brain damage, due to lack of oxygen before or right after birth, or problems with brain formation
- Disorders of the muscles, such as muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy (MD) is a group of inherited disorders that cause muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue, which get worse over time.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Disorders that affect the nerves that supply muscles
- Disorders that affect the ability of nerves to send messages to the muscles
- Infections
Genetic or chromosomal disorders, or defects that may cause brain and nerve damage include:
-
Down syndrome
Down syndrome
Down syndrome is a genetic condition in which a person has 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Spinal muscular atrophy
Spinal muscular atrophy
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a group of disorders of the motor neurons (motor cells). These disorders are passed down through families (inherite...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Prader-Willi syndrome
Prader-Willi syndrome
Prader-Willi syndrome is a disease that is present from birth (congenital). It affects many parts of the body. People with this condition feel hung...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Tay-Sachs disease
Tay-Sachs disease
Tay-Sachs disease is a life-threatening disease of the nervous system passed down through families.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Trisomy 13
Trisomy 13
Trisomy 13 (also called Patau syndrome) is a genetic disorder in which a person has 3 copies of genetic material from chromosome 13, instead of the u...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other disorders that can lead to the condition include:
-
Achondroplasia
Achondroplasia
Achondroplasia is a disorder of bone growth that causes the most common type of dwarfism.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Being born with hypothyroidism
Being born with hypothyroidism
Neonatal hypothyroidism is decreased thyroid hormone production in a newborn. In very rare cases, no thyroid hormone is produced. The condition is ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Poisons or toxins
- Spinal cord injuries that occur around the time of birth
Home Care
Take extra care when lifting and carrying a person with hypotonia to avoid causing an injury.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your health care provider will do a physical exam including a detailed examination of the nervous system and muscle function.
In most cases, a neurologist (specialist in brain and nerve disorders) will help evaluate the problem. Geneticists may help diagnose certain disorders. If there are also other medical problems, a number of different specialists will help care for the child.
Which diagnostic tests are done depends on the suspected cause of the hypotonia. Most of the conditions associated with hypotonia also cause other symptoms that can help make the diagnosis.
Many of these disorders require ongoing care and support. Physical therapy may be recommended to help children improve their development.
References
Barkoudah E. Encephalopathies In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 638.
Burnette WB. Hypotonic (floppy) infant. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 30.
Manzur AY. Evaluation and investigation of neuromuscular disorders. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 647.
Marcdante KJ, Kliegman RM, Schuh AM. Weakness and hypotonia. In: Marcdante KJ, Kliegman RM, Schuh AM, eds. Nelson Essentials of Pediatrics. 9th ed. Elsevier; 2023:chap 182.
-
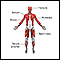
Hypotonia - illustration
Hypotonia is an abnormal neurological sign in newborn or older infants, and may suggest central nervous system dysfunction, genetic disorders, or muscle disorders. Infants with hypotonia rest with their elbows and knees loosely extended. Infants with normal tone tend to have slightly bent elbows and knees. Head control may be poor or absent in children with hypotonia with the head falling to the side, backward, or forward.
Hypotonia
illustration
-
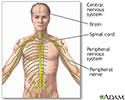
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
-
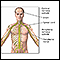
Hypotonia - illustration
Hypotonia is an abnormal neurological sign in newborn or older infants, and may suggest central nervous system dysfunction, genetic disorders, or muscle disorders. Infants with hypotonia rest with their elbows and knees loosely extended. Infants with normal tone tend to have slightly bent elbows and knees. Head control may be poor or absent in children with hypotonia with the head falling to the side, backward, or forward.
Hypotonia
illustration
-
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Anna C. Edens Hurst, MD, MS, Associate Professor in Medical Genetics, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.