Fontanelles - bulging
Soft spot - bulging; Bulging fontanellesA bulging fontanelle is an outward curving of an infant's soft spot (fontanelle).
Considerations
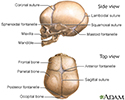
The skull is made up of many bones. There are 8 bones in the skull itself and 14 bones in the face area. They join together to form a solid, bony cavity that protects and supports the brain. The areas where the bones join together are called the sutures.
The bones are not joined together firmly at birth. This allows the head to change shape to help it pass through the birth canal. The sutures get minerals added to them over time and harden, firmly joining the skull bones together.
In an infant, the space where 2 sutures join forms a membrane-covered "soft spot" called a fontanelle (fontanel). The fontanelles allow for growth of the brain and skull during an infant's first year.
There are normally several fontanelles on a newborn's skull. They are located mainly at the top, back, and sides of the head. Like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas.
- The fontanelle in the back of the head (posterior fontanelle) most often closes by age 1 to 2 months.
- The fontanelle at the top of the head (anterior fontanelle) most often closes within 7 to 19 months.
Anterior
Anterior means "in front of" or "the front surface of. " It usually refers to the front side of the body. For example, your knee caps are on the ant...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
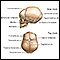
The fontanelles should feel firm and very slightly curved inward to the touch. A tense or bulging fontanelle occurs when fluid builds up in the brain or the brain swells, causing increased pressure inside the skull.
When the infant is crying, lying down, or vomiting, the fontanelles may look like they are bulging. However, they should return to normal when the infant is in a calm, head-up position.
Causes
Reasons a child may have bulging fontanelles include:
-
Encephalitis. Swelling (inflammation) of the brain, most often due to infections.
Encephalitis
Encephalitis is irritation and swelling (inflammation) of the brain, most often due to infections.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hydrocephalus. A buildup of fluid inside the skull.
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to the brain pushing against the skull. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Increased intracranial pressure.
-
Meningitis. Infection of the membranes covering the brain.
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Home Care
If the fontanelle returns to normal appearance when the child is calm and head-up, it is not a truly bulging fontanelle.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Immediate, emergency care is needed for any infant who has a truly bulging fontanelle, especially if it occurs along with fever or excess drowsiness.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask questions about the child's medical history, such as:
Physical exam
During a physical examination, a health care provider checks your body to determine if you do or do not have a physical problem. A physical examinati...
- Does the "soft spot" return to normal appearance when the infant is calm or head-up?
- Does it bulge all the time or does it come and go?
- When did you first notice this?
- Which fontanelles bulge (top of the head, back of the head, or other)?
- Are all the fontanelles bulging?
- What other symptoms are present (such as fever, irritability, or lethargy)?
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleIrritability
Young children who cannot talk yet will let you know when something is wrong by acting fussy or irritable. If your child is fussier than usual, it c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleLethargy
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Diagnostic tests that may be done are:
-
CT scan of the head
CT scan of the head
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
MRI scan of the head
MRI scan of the head
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Spinal tap (lumbar puncture)
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Parga-Belinkie JJ. The newborn infant. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 115.
Rosenberg GA. Brain edema and disorders of cerebrospinal fluid circulation. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 88.
Schnapp BH, Jewell C. Central nervous system infections. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 95.
-
Skull of a newborn - illustration
The sutures or anatomical lines where the bony plates of the skull join together can be easily felt in the newborn infant. The diamond shaped space on the top of the skull and the smaller space further to the back are often referred to as the soft spot in young infants.
Skull of a newborn
illustration
-
Bulging fontanelles - illustration
A tense or bulging fontanelle occurs when fluid accumulates in the skull cavity or when pressure increases in the brain. Common causes are hydrocephalus or increased intracranial pressure due to illness.
Bulging fontanelles
illustration
-
Skull of a newborn - illustration
The sutures or anatomical lines where the bony plates of the skull join together can be easily felt in the newborn infant. The diamond shaped space on the top of the skull and the smaller space further to the back are often referred to as the soft spot in young infants.
Skull of a newborn
illustration
-
Bulging fontanelles - illustration
A tense or bulging fontanelle occurs when fluid accumulates in the skull cavity or when pressure increases in the brain. Common causes are hydrocephalus or increased intracranial pressure due to illness.
Bulging fontanelles
illustration
Review Date: 1/17/2025
Reviewed By: Charles I. Schwartz, MD, FAAP, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, General Pediatrician at PennCare for Kids, Phoenixville, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.