Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection
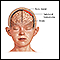
Spinal tap; Ventricular puncture; Lumbar puncture; Cisternal puncture; Cerebrospinal fluid cultureCerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the brain and spine from injury. The fluid is normally clear. It has the same consistency as water. The test is also used to measure pressure in the spinal fluid.
How the Test is Performed
There are different ways to get a sample of CSF. Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) is the most common method.
To have the test:
- You will lie on your side with your knees pulled up toward the chest, and chin tucked downward. Sometimes the test is done sitting up, but bent forward.
- After the back is cleaned, your health care provider will inject a local numbing medicine (anesthetic) into the lower spine.
- A spinal needle will be inserted.
- An opening pressure is sometimes taken. An abnormal pressure may indicate an infection or other problem.
- Once the needle is in position, and after the CSF pressure is measured, a sample of 1 to 10 milliliters (mL) of CSF is collected in 4 or more vials.
- The needle is removed, the area is cleaned, and a bandage is placed over the needle site. You may be asked to remain lying down for a short time after the test.
In some cases, special x-rays are used to help guide the needle into position. This is called fluoroscopy. In other cases, ultrasound can help direct the position of the needle.
Lumbar puncture with fluid collection may also be part of other procedures such as an x-ray or CT scan after dye has been inserted into the CSF.
x-ray
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...

CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan of the thoracic spine is an imaging method. It uses x-rays to rapidly create detailed pictures of the middle back (t...
Rarely, other methods of CSF collection may be used.
- Cisternal puncture uses a needle placed below the occipital bone (back of the skull). It can be dangerous because it is so close to the brain stem. It is always done with fluoroscopy or other imaging guidance.
- Ventricular puncture may be recommended in people with possible brain herniation. It is most often done in the operating room. A hole is drilled in the skull, and a needle is inserted directly into one of the brain's ventricles.
CSF may also be collected from a tube that is already placed in the fluid, such as a shunt or a ventricular drain.
How to Prepare for the Test
You will need to give your health care team your consent before the test. Tell your provider if you are on any aspirin or any other blood-thinning medicines.
After the procedure, you should plan to rest for several hours, even if you feel fine. This is to prevent fluid from leaking around the site of the puncture. You will not need to lie flat on your back the entire time. If you develop a headache, it may be helpful to drink caffeinated beverages such as coffee, tea or soda.
How the Test will Feel
It may be uncomfortable to stay in position for the test. Staying still is important because movement may lead to injury of the spinal cord.
You may be told to straighten your position slightly after the needle is in place. This is to help measure the CSF pressure.
The anesthetic will sting or burn when first injected. There will be a hard pressure sensation when the needle is inserted. Often, there is some brief discomfort when the needle goes through the tissue surrounding the spinal cord. This pain should stop in a few seconds.
In most cases, the procedure takes about 30 minutes. The actual pressure measurements and CSF collection only take a few minutes.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to measure pressures within the CSF and to collect a sample of the fluid for further testing.
CSF analysis can be used to diagnose certain neurologic disorders. These may include infections (such as meningitis) and brain or spinal cord damage. A spinal tap may also be done to establish the diagnosis of normal pressure hydrocephalus or bleeding into the spinal fluid from an aneurysm.
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.

Normal pressure hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of spinal fluid inside the fluid chambers of the brain. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "Normal pressure hydroce...
Aneurysm
An aneurysm is an abnormal widening or ballooning of a part of an artery due to weakness in the wall of the blood vessel.

Normal Results
Normal values typically range as follows:
- Pressure: 90 to 180 mm H2O
- Appearance: clear, colorless
-
CSF total protein: 15 to 60 mg/dL (0.15 to 0.60 g/L)
CSF total protein
CSF total protein is a test to determine the amount of protein in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is a clear fluid that is in the space around the sp...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Gamma globulin: 3% to 12% of the total protein
Total protein
The total protein test measures the total amount of two classes of proteins found in the fluid portion of your blood. These are albumin and globulin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CSF glucose: 50 to 80 mg/100 mL or 2.77 to 4.44 mmol/L (or greater than two thirds of blood sugar level)
CSF glucose
A CSF glucose test measures the amount of sugar (glucose) in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is a clear fluid that flows in the space surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CSF cell count: 0 to 5 white blood cells (all mononuclear), and no red blood cells
CSF cell count
A CSF cell count is a test to measure the number of red and white blood cells that are in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is a clear fluid that is in...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chloride: 115 to 130 mEq/L
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different labs. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
The examples above show the common measurements for results for these tests. Some labs use different measurements or may test different specimens.
What Abnormal Results Mean
If the CSF looks cloudy, it could mean there is an infection or a buildup of white blood cells or protein.
If the CSF looks bloody or red, it may be a sign of bleeding or spinal cord obstruction. If it is brown, orange, or yellow, it may be a sign of increased CSF protein or previous bleeding (more than 3 days ago). There may be blood in the sample that came from the spinal tap itself. This makes it harder to interpret the test results.
CSF PRESSURE
- Increased CSF pressure may be due to increased intracranial pressure (pressure within the skull).
Increased intracranial pressure
Increased intracranial pressure is a rise in the pressure inside the skull that can result from or cause brain injury.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Decreased CSF pressure may be due to spinal block, dehydration, or CSF leakage.
Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when your body does not have as much water and fluids as it needs. Dehydration can be mild, moderate, or severe, based on how much...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
CSF PROTEIN
- Increased CSF protein may be due to blood in the CSF, diabetes, polyneuritis, tumor, injury, or any inflammatory or infectious condition.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleTumor
A tumor is an abnormal growth of body tissue. Tumors can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Decreased protein is a sign of rapid CSF production or systemic loss of protein.
CSF GLUCOSE
- Increased CSF glucose is a sign of high blood sugar.
- Decreased CSF glucose may be due to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), bacterial or fungal infection (such as meningitis), tuberculosis, or certain other types of meningitis.
Hypoglycemia
Low blood sugar is a condition that occurs when the body's blood sugar (glucose) decreases and is too low. Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL (3. 9 mmol/L) i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMeningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
BLOOD CELLS IN CSF
- Increased white blood cells in the CSF may be a sign of meningitis, acute infection, beginning of a long-term (chronic) illness, tumor, abscess, or demyelinating disease (such as multiple sclerosis).
Acute
Acute means sudden. Acute symptoms appear, change, or worsen rapidly. It is the opposite of chronic.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAbscess
An abscess is a collection of pus in any part of the body. In most cases, the area around an abscess is swollen and inflamed.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Red blood cells in the CSF sample may be a sign of bleeding into the spinal fluid or the result of a traumatic lumbar puncture.
OTHER CSF RESULTS
- Increased CSF gamma globulin levels may be due to diseases such as multiple sclerosis, neurosyphilis, or Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease that affects the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleNeurosyphilis
Neurosyphilis is a bacterial infection of the brain or spinal cord. It usually occurs in people who have had untreated syphilis for many years....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleGuillain-Barré syndrome
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a serious health problem that occurs when the body's defense (immune) system mistakenly attacks part of the peripher...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Additional conditions under which the test may be performed:
-
Chronic inflammatory polyneuropathy
Chronic inflammatory polyneuropathy
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is a disorder that involves nerve swelling and irritation (inflammation) that leads to a los...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Dementia due to metabolic causes
Dementia due to metabolic causes
Dementia is loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases. Dementia may also be referred to as major neurocognitive disorder. Dementia du...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Encephalitis
Encephalitis
Encephalitis is irritation and swelling (inflammation) of the brain, most often due to infections.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Epilepsy
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a brain disorder in which a person has repeated seizures over time. Seizures are episodes of uncontrolled and abnormal electrical activi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Febrile seizure (children)
Febrile seizure (children)
A febrile seizure is a convulsion in a child triggered by a fever.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Generalized tonic-clonic seizure
Generalized tonic-clonic seizure
Bilateral tonic-clonic seizure is a type of seizure that involves the entire body. It is also called grand mal seizure. The terms generalized seizu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to the brain pushing against the skull. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "...
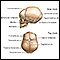 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH)
Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH)
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of spinal fluid inside the fluid chambers of the brain. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "Normal pressure hydroce...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pituitary tumor
Pituitary tumor
A pituitary tumor is an abnormal growth in the pituitary gland. The pituitary is a small gland at the base of the brain. It regulates the body's ba...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Reye syndrome
Reye syndrome
Reye syndrome is characterized by sudden (acute) brain damage and liver function problems. This condition does not have a known cause. This syndrome...
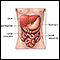 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
Risks of lumbar puncture include:
- Bleeding into the spinal canal or around the brain (subdural hematomas).
Subdural hematomas
A subdural hematoma is a collection of blood between the covering of the brain (dura) and the surface of the brain.
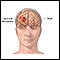 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Discomfort during the test.
- Headache after the test that can last a few hours or days. It may be helpful to drink caffeinated beverages such as coffee, tea or soda to help relieve the headache. If headaches last more than a few days (especially when you sit, stand or walk) you might have a CSF-leak. You should talk to your provider if this occurs.
- Hypersensitivity (allergic) reaction to the anesthetic.
- Infection introduced by the needle going through the skin.
Brain herniation may occur if this test is done on a person with a mass in the brain (such as a tumor or abscess). This can result in brain damage or death. This test is not done if an exam or test reveals signs of a brain mass.
Damage to the nerves in the spinal cord may occur, particularly if the person moves during the test.
Cisternal puncture or ventricular puncture carries additional risks of brain or spinal cord damage and bleeding within the brain.
Considerations
This test is more dangerous for people with:
- A tumor in the back of the brain that is pressing down on the brainstem
- Blood clotting problems
- Low platelet count (thrombocytopenia)
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia means there is an abnormally low amount of platelets. Platelets are parts of the blood that help blood to clot. This condition is ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Individuals taking blood thinners, aspirin, clopidogrel, or other similar medicines to decrease the formation of blood clots.
References
De Luca GC, Griggs RC, Johnston SC. Approach to the patient with neurologic disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 366.
Karcher DS, McPherson RA. Cerebrospinal, synovial, serous body fluids, and alternative specimens. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022: chap 30.
Rosenberg GA. Brain edema and disorders of cerebrospinal fluid circulation. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 88.
Schnapp BH, Jewell C. Central nervous system infections. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 95.
-
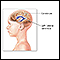
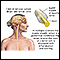
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) - illustration
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is a procedure to collect cerebrospinal fluid to check for the presence of disease or injury. A spinal needle is inserted, usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae in the lower spine. Once the needle is properly positioned in the subarachnoid space (the space between the spinal cord and its covering, the meninges), pressures can be measured and fluid can be collected for testing.
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
illustration
-
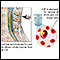
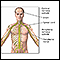
CSF chemistry - illustration
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear fluid that circulates in the space surrounding the spinal cord and brain. CSF protects the brain and spinal cord from injury by acting like a liquid cushion. CSF is usually obtained through a lumbar puncture (spinal tap). During the procedure, a needle is inserted usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae and the CSF fluid is collected for testing.
CSF chemistry
illustration
-
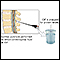
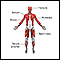
Lumbar vertebrae - illustration
There are 5 lumbar vertebrae located in the lower back. These vertebrae receive the most stress and are the weight-bearing portion of the back. The lumbar vertebrae allow movements such as flexion and extension and some lateral flexion.
Lumbar vertebrae
illustration
-
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) - illustration
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is a procedure to collect cerebrospinal fluid to check for the presence of disease or injury. A spinal needle is inserted, usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae in the lower spine. Once the needle is properly positioned in the subarachnoid space (the space between the spinal cord and its covering, the meninges), pressures can be measured and fluid can be collected for testing.
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
illustration
-
CSF chemistry - illustration
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear fluid that circulates in the space surrounding the spinal cord and brain. CSF protects the brain and spinal cord from injury by acting like a liquid cushion. CSF is usually obtained through a lumbar puncture (spinal tap). During the procedure, a needle is inserted usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae and the CSF fluid is collected for testing.
CSF chemistry
illustration
-
Lumbar vertebrae - illustration
There are 5 lumbar vertebrae located in the lower back. These vertebrae receive the most stress and are the weight-bearing portion of the back. The lumbar vertebrae allow movements such as flexion and extension and some lateral flexion.
Lumbar vertebrae
illustration
Review Date: 4/16/2025
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.




