Epstein-Barr virus antibody test
EBV antibody test; EBV serology; Mono testEpstein-Barr virus antibody test is a blood test to detect antibodies to the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which is a cause of the infectious disease mononucleosis.
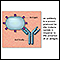
Antibodies
An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. Examples of antigens include micr...
Mononucleosis
Mononucleosis, or mono, is a viral infection that causes fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands, most often in the neck.

How the Test is Performed
Blood sample is needed
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.

The sample is sent to a lab, where a lab specialist looks for antibodies to EBV. In the first stages of an illness, little or no antibodies may be detected. For this reason, the test is often repeated in 10 days to 2 or more weeks.
How to Prepare for the Test
There is no special preparation for the test.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or slight bruising. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
The test is done to detect an infection with EBV. EBV causes mononucleosis or mono. The EBV antibody test detects not only a recent infection, but also one that occurred in the past. It can be used to tell the difference between a recent and a previous infection.
Another test for mononucleosis is called the Monospot test. It is often done when a person has current symptoms of mononucleosis.
Monospot test
The mononucleosis spot test looks for 2 antibodies in the blood. These antibodies appear during or after an infection with the virus that causes mon...

Normal Results
A normal result means no antibodies to EBV were seen in your blood sample. This result means you have never been infected with EBV.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different labs. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A positive result means there are antibodies to EBV in your blood. This indicates a current or prior infection with EBV.
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Johannsen EC, Kaye KM. Epstein-Barr virus (infectious mononucleosis, Epstein-Barr virus-associated malignant diseases, and other diseases). In: Blaser MJ, Cohen JI, Holland SM, et al, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2026:chap 145.
Plourde AR, Beavis KG. Specimen collection and handling for diagnosis of infectious diseases. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022: chap 66.
-
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
-
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
Review Date: 8/5/2025
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Roy and Diana Vagelos Professor in Medicine, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, New York, NY. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


