Complement component 3 (C3)
C3Complement C3 is a blood test that measures the activity of a certain protein.
This protein is part of the complement system. The complement system is a group of nearly 60 proteins that are in blood plasma or on the surface of some cells. The proteins work with your immune system and play a role to protect the body from infections, and to remove dead cells and foreign material. Rarely, people may inherit deficiency of one or more complement proteins. These people are prone to certain infections or autoimmune disorders.
Complement system
Complement is a blood test that measures the activity of certain proteins in the liquid portion of your blood. The complement system is a group of ne...

There are nine major complement proteins. They are labeled C1 through C9. This article describes the test that measures C3.
How the Test is Performed
Blood is drawn from a vein. Most often, a vein from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand is used.
The procedure is as follows:
- The site is cleaned with an antiseptic.
- The health care provider wraps an elastic band around the upper arm to apply pressure to the area and make the vein swell with blood.
- The provider gently inserts a needle into the vein.
- The blood collects into an airtight vial or tube attached to the needle. The elastic band is removed from your arm.
- Once the blood has been collected, the needle is removed. The puncture site is covered to stop any bleeding.
In infants or young children, a sharp tool called a lancet may be used to puncture the skin and make it bleed. The blood collects into a small glass tube called a pipette, or onto a slide or test strip. A bandage may be placed over the area if there is any bleeding.
How to Prepare for the Test
There is no special preparation needed.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others may feel only a prick or stinging sensation. Afterward, there may be some throbbing.
Why the Test is Performed
C3 and C4 are the most commonly measured complement components.
A complement test may be used to monitor people with an autoimmune disorder. It is done to see if treatment for their condition is working. When the complement system is turned on during inflammation, levels of complement proteins may go down. For example, people with active lupus erythematosus may have lower-than-normal levels of the complement proteins C3 and C4.
Autoimmune disorder
An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune d...
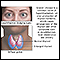
Lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It c...
C3
Complement C3 is a blood test that measures the activity of a certain protein. This protein is part of the complement system. The complement system ...

C4
Complement component 4 is a blood test that measures the activity of a certain protein. This protein is part of the complement system. The compleme...

The test may also be done for the following conditions:
- Fungal infections
- Gram negative septicemia
Septicemia
Septicemia is an infection in the bloodstream that is caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Also called sepsis, septicemia is a serious, life-threa...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Parasitic infections, such as malaria
Malaria
Malaria is a parasitic disease that involves high fevers, shaking chills, flu-like symptoms, and anemia.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH)
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PN...
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria is a rare disease in which red blood cells break down earlier than normal.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Shock
Shock
Shock is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body is not getting enough blood flow. Lack of blood flow means the cells and organs do n...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Normal Results
The normal range is 88 to 201 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) (0.88 to 2.01 g/L).
Note: Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
The examples above show the common measurements for results for these tests. Some laboratories use different measurements or may test different specimens.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Increased complement activity may be seen in:
-
Cancer
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
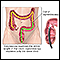
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a condition in which the lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum become inflamed. It is a form of inflammatory bowel ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Decreased complement activity may be seen in:
- Bacterial infections (especially Neisseria)
-
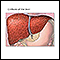
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver and poor liver function. It is the last stage of chronic liver disease.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is a type of kidney disease in which the part of your kidneys that helps filter waste and fluids from the blood is damaged....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hepatitis
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is swelling and inflammation of the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hereditary angioedema
Hereditary angioedema
Hereditary angioedema is a rare but serious problem with the immune system. The problem is passed down through families. It causes swelling, partic...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Kidney transplant rejection
Kidney transplant
A kidney transplant is surgery to place a healthy kidney into a person with kidney failure.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Lupus nephritis
Lupus nephritis
Lupus nephritis, which is a kidney disorder, is a complication of systemic lupus erythematosus.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Malnutrition
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Rare inherited complement deficiencies
- Systemic vasculitis
Risks
Risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
-
Fainting or feeling lightheaded
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
Hematoma
A bruise is an area of skin discoloration. A bruise occurs when small blood vessels break and leak their contents into the soft tissue beneath the s...
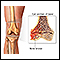 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Considerations
The complement cascade is a series of reactions that take place in the blood. The cascade activates the complement proteins. The result is an attack unit that creates holes in the membrane of bacteria, killing them. C3 attaches to bacteria and kills them directly.
References
Atkinson JP, Holers VM. Complement system in disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 37.
Bean KV, Massey HD, Gupta G. Mediators of inflammation: complement. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 48.
Ram S. Complement and deficiencies. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 9.
Sullivan KE, Grumach AS. The complement system. In: Burks AW, Holgate ST, O'Hehir RE, et al, eds. Middleton's Allergy: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 8.
-
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
-
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
Review Date: 1/28/2025
Reviewed By: Diane M. Horowitz, MD, Rheumatology and Internal Medicine, Northwell Health, Great Neck, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


