Aldolase blood test
Aldolase is a protein (called an enzyme) that helps break down certain sugars to produce energy. It is found in high amount in muscle and liver tissue.
A test can be done to measure the amount of aldolase in your blood.
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed.
Blood sample
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.

How to Prepare for the Test
You may be told not to eat or drink anything for 6 to 12 hours before the test. You may be also told to avoid vigorous exercise for 12 hours before the test. Your health care provider will tell you if it is necessary to stop taking any medicines that may interfere with this test. Tell your provider about all the medicines you are taking, both prescription and nonprescription.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or slight bruising. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to diagnose or monitor muscle or liver damage.
Other tests that may be ordered to check for liver damage include:
-
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) test
Alanine aminotransferase
The alanine transaminase (ALT) blood test measures the level of the enzyme ALT in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) test
Aspartate aminotransferase
The aspartate aminotransferase (AST) blood test measures the level of the enzyme AST in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other tests that may be ordered to check for muscle cell damage include:
-
Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) test
Creatine phosphokinase
Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) is an enzyme in the body. It is found mainly in the heart, brain, and skeletal muscle. This article discusses the test...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) test
Lactate dehydrogenase
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is a protein that helps produce energy in the body. An LDH test measures the amount of LDH in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
In some cases of myositis, especially dermatomyositis, aldolase level may be elevated even when CPK is normal.
Myositis
Myositis is an inflammation or swelling of the muscles. It is most often caused by injury, infection, medicines, or an autoimmune disorder. Dermatom...
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is a disease that involves muscle inflammation and a skin rash. Polymyositis is a similar inflammatory condition that also involves ...

Normal Results
Normal results range between 1.0 to 7.5 units per liter (0.02 to 0.13 microkat/L). There is a slight difference between men and women.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A higher than normal level may be due to:
- Damage to skeletal muscles
-
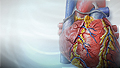
Heart attack
Heart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Liver, pancreatic, or prostate cancer
Prostate cancer
Myositis is an inflammation or swelling of the muscles. It is most often caused by injury, infection, medicines, or an autoimmune disorder. Dermatom...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Muscle disease such as dermatomyositis, muscular dystrophy, polymyositis
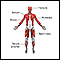
Muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy (MD) is a group of inherited disorders that cause muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue, which get worse over time.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePolymyositis
Polymyositis and dermatomyositis are rare inflammatory diseases. These diseases lead to muscle weakness, swelling, tenderness, and tissue damage. T...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Swelling and inflammation of the liver (hepatitis)
Swelling
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHepatitis
Hepatitis is swelling and inflammation of the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Viral infection called mononucleosis
Mononucleosis
Mononucleosis, or mono, is a viral infection that causes fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands, most often in the neck.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
-
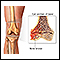
Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
Hematoma
A bruise is an area of skin discoloration. A bruise occurs when small blood vessels break and leak their contents into the soft tissue beneath the s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Panteghini M. Serum enzymes. In: Rifai N, Chiu RWK, Young I, Burnham Carey-Ann D, Wittwer CT, eds. Tietz Textbook of Laboratory Medicine. 7th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 32.
Vleugels RA, Jorizzo JL. Dermatomyositis. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 42.
-
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
-
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Neil J. Gonter, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Columbia University, NY and private practice specializing in Rheumatology at Rheumatology Associates of North Jersey, Teaneck, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


