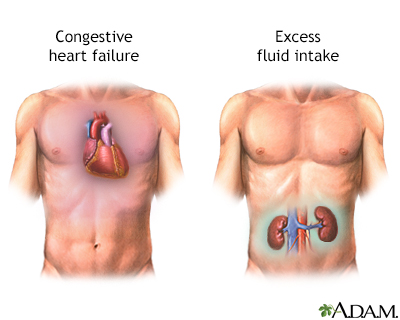
Osmolality urine test
The osmolality urine test measures the concentration of chemicals in urine.
Osmolality in the blood can be measured using a blood test.
Blood test
Osmolality blood test is a test that measures the concentration of all chemical particles found in the fluid part of blood. Osmolality in the urine c...

How the Test is Performed
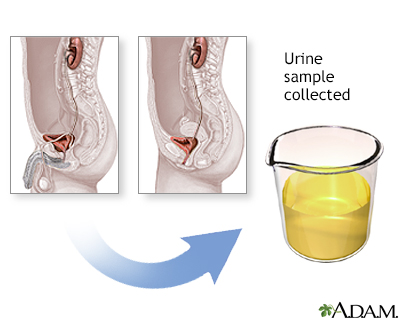
A clean-catch urine sample is needed. The clean-catch method is used to prevent germs from the penis or vagina from getting into a urine sample. To collect your urine, your health care provider may give you a special clean-catch kit that contains a cleansing solution and sterile wipes. Follow instructions exactly.
Clean-catch urine sample
A clean catch is a method of collecting a urine sample to be tested. The clean-catch urine method is used to prevent germs from the penis or vagina ...
How to Prepare for the Test
Your provider may tell you that you need to limit your fluid intake 12 to 14 hours before the test.
Your provider will ask you to temporarily stop taking any medicines that may affect the test results. Be sure to tell your provider about all the medicines you take, including dextran and sucrose. Do not stop taking any medicine before talking to your provider.
Other things can also affect the test results. Tell your provider if you recently:
- Had any type of anesthesia for an operation.
- Received intravenous dye (contrast medium) for an imaging test such as a CT scan or MRI.
CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Used herbs or natural remedies, especially Chinese herbs.
How the Test will Feel
The test involves normal urination. There is no discomfort.
Why the Test is Performed
This test helps check your body's water balance and urine concentration.
Urine osmolality is a more exact measurement of urine concentration than the urine specific gravity test.
Urine specific gravity
Urine specific gravity is a laboratory test that shows the total concentration of all chemical particles in the urine.

Normal Results
Normal values are as follows:
- Random specimen: 50 to 1200 mOsm/kg (50 to 1200 mmol/kg)
- 12 to 14 hour fluid restriction: Greater than 850 mOsm/kg (850 mmol/kg)
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results are indicated as follows:
Higher than normal osmolality may indicate:
- Adrenal glands do not produce enough hormones (Addison disease or other types of adrenal insufficiency)
Addison disease
Addison disease is a disorder that causes the adrenal glands to not produce enough hormones.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Glucose (a type of sugar) in the urine
-
Heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - High sodium level in the blood
-
Loss of body fluids (dehydration)
Loss of body fluids
Dehydration occurs when your body does not have as much water and fluids as it needs. Dehydration can be mild, moderate, or severe, based on how much...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Narrowing of the kidney artery (renal artery stenosis)
-
Shock
Shock
Shock is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body is not getting enough blood flow. Lack of blood flow means the cells and organs do n...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion (SIADH)
SIADH
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) is a condition in which the body makes too much antidiuretic hormone (ADH). ADH is ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Lower than normal osmolality may indicate:
- Damage to kidney tubule cells (renal tubular necrosis)
Renal tubular necrosis
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) is a kidney disorder involving damage to the tubule cells of the kidneys, which can lead to acute kidney failure. The t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus (DI) is an uncommon condition in which the kidneys are unable to prevent the excretion of water. DI is not the same as diabetes me...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Drinking too much fluid
- Kidney failure
- Low sodium level in the blood
- Severe kidney infection (pyelonephritis)
Risks
There are no risks with this test.
References
Kashkouli A, Berl T, Sands JM. Disorders of water metabolism. In: Johnson RJ, Floege J, Tonelli M, eds. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 9.
Oh MS, Briefel G, Pincus MR. Evaluation of renal function, water, electrolytes, and acid-base balance. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 15.
-
Osmolality test - illustration
An osmolality urine test is performed to measure the concentration of particles in urine. Greater than normal results may indicate conditions such as Addison disease, congestive heart failure or shock. Lower-than-normal measurements may indicate aldosteronism, diabetes insipidus, excess fluid intake, renal tubular necrosis or severe pyelonephritis.
Osmolality test
illustration
-
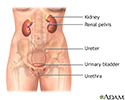
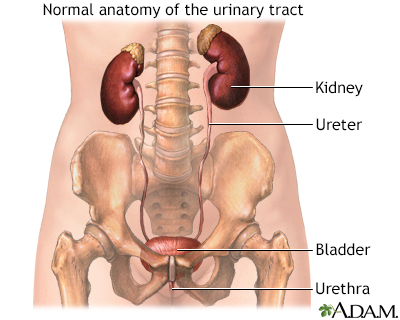
Female urinary tract - illustration
The female and male urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Female urinary tract
illustration
-
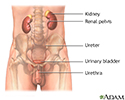
Male urinary tract - illustration
The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Male urinary tract
illustration
-
Osmolality urine - series
Presentation
-
Osmolality test - illustration
An osmolality urine test is performed to measure the concentration of particles in urine. Greater than normal results may indicate conditions such as Addison disease, congestive heart failure or shock. Lower-than-normal measurements may indicate aldosteronism, diabetes insipidus, excess fluid intake, renal tubular necrosis or severe pyelonephritis.
Osmolality test
illustration
-
Female urinary tract - illustration
The female and male urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Female urinary tract
illustration
-
Male urinary tract - illustration
The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Male urinary tract
illustration
-
Osmolality urine - series
Presentation
Review Date: 8/20/2023
Reviewed By: Jacob Berman, MD, MPH, Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of General Internal Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.