Sputum fungal smear
KOH test; Fungal smear - sputum; Fungal wet prep; Wet prep - fungalA sputum fungal smear is a laboratory test that looks for fungus in a sputum sample. Sputum is the material that comes up from air passages when you cough deeply.
How the Test is Performed
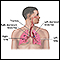
A sputum sample is needed. You will be asked to cough deeply and spit any material that comes up from your lungs into a special container.
The sample is sent to a lab and examined under a microscope.
How to Prepare for the Test
There is no special preparation.
How the Test will Feel
There is no discomfort.
Why the Test is Performed
Your health care provider may order this test if you have symptoms or signs of a lung infection, such as if you have a weakened immune system due to certain medicines or diseases such as cancer or HIV/AIDS.
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...

Normal Results
A negative result means no fungus was seen in the test sample.
Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may be a sign of a fungal infection. Such infections include:
-
Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is an infection or allergic response due to the aspergillus fungus.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis is an infection caused by breathing in the Blastomyces dermatitidis fungus. This fungus is found in decaying wood and soil.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis
Valley fever is an infection that occurs when the spores of the fungus Coccidioides immitis or Coccidioides posadasii enter your body through the lun...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cryptococcosis
Cryptococcosis
Cryptococcosis is infection with the fungi Cryptococcus neoformans or Cryptococcus gattii.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis is an infection that occurs from breathing in the spores of the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
There are no risks associated with a sputum fungal smear.
References
Banaei N, Deresinski SC, Pinsky BA. Microbiologic diagnosis of lung infection. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 19.
Saullo JL, Alexander BD. Fungal infections: opportunistic. In: Broaddus VC, King TE, Ernst JD, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 57.
-
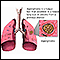
Sputum test - illustration
A sputum sample is obtained by coughing deeply and expelling the material that comes from the lungs into a specimen container. The sample is transferred to a slide and examined under a microscope. A positive result indicates a fungal infection in the lungs.
Sputum test
illustration
-
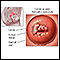
Fungus - illustration
Fungal infections are caused by microscopic organisms (fungi) that can live on the skin. They can live on the dead tissues of the hair, nails, and outer skin layers.
Fungus
illustration
-
Sputum test - illustration
A sputum sample is obtained by coughing deeply and expelling the material that comes from the lungs into a specimen container. The sample is transferred to a slide and examined under a microscope. A positive result indicates a fungal infection in the lungs.
Sputum test
illustration
-
Fungus - illustration
Fungal infections are caused by microscopic organisms (fungi) that can live on the skin. They can live on the dead tissues of the hair, nails, and outer skin layers.
Fungus
illustration
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Roy and Diana Vagelos Professor in Medicine, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, New York, NY. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.



