Abdominal ultrasound
Ultrasound - abdomen; Abdominal sonogram; Right upper quadrant sonogramAbdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys. The blood vessels that lead to some of these organs, such as the inferior vena cava and aorta, can also be examined with ultrasound.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of organs and structures inside the body.
How the Test is Performed
An ultrasound machine makes images of organs and structures inside the body. The machine sends out high-frequency sound waves that reflect off body structures. A computer receives these waves and uses them to create a picture. Unlike with x-rays or CT scans, this test does not expose you to ionizing radiation.
x-rays
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...

CT scans
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...

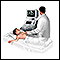
You will be lying down for the procedure. A clear, water-based conducting gel is applied to the skin over the abdomen. This helps with the transmission of the sound waves. A handheld probe called a transducer is then moved over the abdomen.
You may need to change position so that the health care provider can look at different areas. You may also need to hold your breath for short periods during the exam.
Most of the time, the test takes less than 30 minutes.
How to Prepare for the Test
How you will prepare for the test depends on the problem. You will likely be asked not to eat or drink for several hours before the exam. Your health care provider will go over what you need to do.
How the Test will Feel
There is little discomfort. The conducting gel may feel a little cold and wet. The sonographer may press the probe against your abdomen.
Why the Test is Performed
You may have this test to:
- Find the cause of abdominal pain
- Find the cause of kidney infections
- Diagnose or monitor tumors and cancers
- Diagnose or treat ascites
Ascites
Ascites is the build-up of fluid in the space between the lining of the abdomen and abdominal organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Learn why there is swelling of an abdominal organ
- Look for damage after an injury
- Look for stones in the gallbladder or kidney
- Look for the cause of abnormal blood tests such as liver function tests or kidney tests
Liver function tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsinAlkaline phosphata...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Look for the cause of a fever
The reason for the test will depend on your symptoms.
Normal Results
The organs examined appear normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
The meaning of abnormal results depends on the organ being examined and the type of problem. Talk to your provider if you have any questions or concerns.
An abdominal ultrasound can indicate conditions such as:
-
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
The aorta is the main blood vessel that supplies blood to the abdomen, pelvis, and legs. An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) occurs when an area of t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Abscess
Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus in any part of the body. In most cases, the area around an abscess is swollen and inflamed.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Appendicitis
Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a condition in which your appendix gets inflamed. The appendix is a small pouch attached to the end of the large intestine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
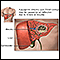
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis
Chronic cholecystitis is swelling and irritation of the gallbladder that continues over time. The gallbladder is a sac located under the liver. It s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Gallstones
Gallstones
Gallstones are hard deposits that form inside the gallbladder. These may be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis is swelling of one kidney due to a backup of urine. This problem may occur in one kidney.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Kidney stones
Kidney stones
A kidney stone is a solid mass made up of tiny crystals. One or more stones can be in the kidney or ureter at the same time.
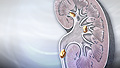 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pancreatitis (inflammation in pancreas)
- Spleen enlargement (splenomegaly)
Splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is a larger-than-normal spleen. The spleen is an organ in the upper left part of the belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Portal hypertension
- Liver tumors
- Obstruction of bile ducts
-
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver and poor liver function. It is the last stage of chronic liver disease.
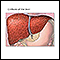 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
There is no known risk. You are not exposed to ionizing radiation.
References
Carucci LR. Diagnostic imaging procedures in gastroenterology. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 119.
Chen L. Abdominal ultrasound imaging: anatomy, physics, instrumentation, and technique. In: Sahani DV, Samir AE, eds. Abdominal Imaging. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 3.
Nickels LC, Duran-Gehring P. Emergency ultrasound. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap e3.
Wilson SR, Medellin A. The gastrointestinal tract. In: Rumack CM, Levine D, eds. Diagnostic Ultrasound. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 8.
-
Abdominal ultrasound - illustration
Abdominal ultrasound is a scanning technique used to image the interior of the abdomen. Like the X-ray, MRI, and CT scan, it has its place as a diagnostic tool. Ultrasound scans use high frequency sound waves to produce an image and do not expose the individual to radiation. The procedure is painless and safe.
Abdominal ultrasound
illustration
-
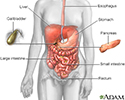
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
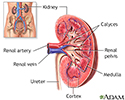
Kidney anatomy - illustration
The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance and blood pressure, and the stimulation of red blood cell production.
Kidney anatomy
illustration
-
Kidney - blood and urine flow - illustration
This is the typical appearance of the blood vessels (vasculature) and urine flow pattern in the kidney. The blood vessels are shown in red and the urine flow pattern in yellow.
Kidney - blood and urine flow
illustration
-
Abdominal ultrasound - illustration
The test is done in the ultrasound or radiology department. A conducting paste is applied to your abdomen while you are lying down. The transducer (a hand-held instrument) is then moved over your abdomen.
Abdominal ultrasound
illustration
-
Abdominal ultrasound - illustration
Abdominal ultrasound is a scanning technique used to image the interior of the abdomen. Like the X-ray, MRI, and CT scan, it has its place as a diagnostic tool. Ultrasound scans use high frequency sound waves to produce an image and do not expose the individual to radiation. The procedure is painless and safe.
Abdominal ultrasound
illustration
-
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
Kidney anatomy - illustration
The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance and blood pressure, and the stimulation of red blood cell production.
Kidney anatomy
illustration
-
Kidney - blood and urine flow - illustration
This is the typical appearance of the blood vessels (vasculature) and urine flow pattern in the kidney. The blood vessels are shown in red and the urine flow pattern in yellow.
Kidney - blood and urine flow
illustration
-
Abdominal ultrasound - illustration
The test is done in the ultrasound or radiology department. A conducting paste is applied to your abdomen while you are lying down. The transducer (a hand-held instrument) is then moved over your abdomen.
Abdominal ultrasound
illustration
Review Date: 7/15/2024
Reviewed By: Jason Levy, MD, FSIR, Northside Radiology Associates, Atlanta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.