Thoracic spine x-ray
Vertebral radiography; X-ray - spine; Thoracic x-ray; Spine x-ray; Thoracic spine films; Back filmsA thoracic spine x-ray is an x-ray of the 12 chest (thoracic) bones (vertebrae) of the spine. The vertebrae are separated by flat pads of cartilage called disks that provide a cushion between the bones.
How the Test is Performed
The test is done in a hospital radiology department or in your health care provider's office. You will lie on the x-ray table in different positions. If the x-ray is checking for an injury, care will be taken to prevent further injury.
The x-ray machine will be moved over the thoracic area of the spine. You will hold your breath as the picture is taken so that the picture will not be blurry. Usually, 2 or 3 x-ray views are needed.
How to Prepare for the Test
Tell your provider if you are pregnant. Also tell your provider if you have had surgery in your chest, abdomen, or pelvis.
Remove all jewelry.
How the Test will Feel
The test causes no discomfort. The table may be cold.
Why the Test is Performed
The x-ray helps evaluate:
- Bone injuries
- Cartilage loss
-
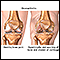
Arthritis
Arthritis
Arthritis is inflammation or degeneration of one or more joints. A joint is the area where 2 bones meet. There are more than 100 different types of...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Curvature in the spine
- Diseases of the bone
- Tumors of the bone
What Abnormal Results Mean
The test can detect:
- Bone spurs
- Deformities of the spine
- Disk narrowing
- Dislocations
- Fractures (most often compression fractures of the vertebrae)
Compression fractures
Compression fractures of the back are broken vertebrae. Vertebrae are the bones of the spine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Thinning of the bone (osteoporosis)
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break (fracture).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Wearing away (degeneration) of the vertebrae
- Abnormal alignment of the bone (spondylolisthesis)
Risks
There is low radiation exposure. X-rays are monitored and regulated to provide the minimum amount of radiation exposure needed to produce the image. Most experts feel that the risk is low compared with the benefits.
Pregnant women and children are more sensitive to the risks of x-rays.
Considerations
The x-ray will not detect problems in the muscles, nerves, and other soft tissues, because these problems cannot be seen well on an x-ray.
References
Preston-Suni K, Kaji AH. Spinal trauma. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 35.
Mettler FA. Skeletal system. In: Mettler FA, ed. Essentials of Radiology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 8.
Van Thielen T, van den Hauwe L, Van Goethem JW, Parizel PM. Current status of imaging of the spine and anatomical features. In: Adam A, Dixon AK, Gillard JH, Schaefer-Prokop CM, eds. Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology: A Textbook of Medical Imaging. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 47.
-
Skeletal spine - illustration
The spine is divided into several sections. The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. The thoracic vertebrae comprise the chest section and have ribs attached. The lumbar vertebrae are the remaining vertebrae below the last thoracic bone and the top of the sacrum. The sacral vertebrae are caged within the bones of the pelvis, and the coccyx represents the terminal vertebrae or vestigial tail.
Skeletal spine
illustration
-
Vertebra, thoracic (mid back) - illustration
These are twelve vertebra of the mid back. The last vertebra (on the left side of the picture) attaches to the lumbar (lower) spine, and the top vertebra (on the right) attaches to the cervical (neck) section of the back. The vertebra are broader and stronger than the cervical bones. This allows them to absorb the added pressure applied to the mid back, but they remain a common sight of injury. The vertebra are numbered from one to twelve and labeled T1, T2, T3, et cetera, from the upper most bones to the lowest.
Vertebra, thoracic (mid back)
illustration
-
Vertebral column - illustration
This is the spine and the sacrum with the cervical (neck), thoracic (mid-back), and lumbar (lower back) vertebra. Notice how the appearance of the vertebra change as you look down the spine. The change in shape and size reflect the different functions of the neck, mid-back, and lower back.
Vertebral column
illustration
-
Intervertebral disk - illustration
The vertebral column is made up of 26 bones that provide axial support to the trunk. The vertebral column provides protection to the spinal cord that runs through its central cavity. Between each vertebra is an intervertebral disk. The disks are filled with a gelatinous substance, called the nucleus pulposus, which provides cushioning to the spinal column. The annulus fibrosus is a fibrocartilageous ring that surrounds the nucleus pulposus, which keeps the nucleus pulposus intact when forces are applied to the spinal column. The intervertebral disks allow the vertebral column to be flexible and act as shock absorbers during everyday activities such as walking, running and jumping.
Intervertebral disk
illustration
-
Anterior skeletal anatomy - illustration
The skeleton is made up of 206 bones in the adult and contributes to the form and shape of the body. The skeleton has several important functions for the body. The bones of the skeleton provide support for the soft tissues. For example, the rib cage supports the thoracic wall. Most muscles of the body are attached to bones which act as levers to allow movement of body parts. The bones of the skeleton also serve as a reservoir for minerals, such as calcium and phosphate. Finally, most of the blood cell formation takes places within the marrow of certain bones.
Anterior skeletal anatomy
illustration
-
Skeletal spine - illustration
The spine is divided into several sections. The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. The thoracic vertebrae comprise the chest section and have ribs attached. The lumbar vertebrae are the remaining vertebrae below the last thoracic bone and the top of the sacrum. The sacral vertebrae are caged within the bones of the pelvis, and the coccyx represents the terminal vertebrae or vestigial tail.
Skeletal spine
illustration
-
Vertebra, thoracic (mid back) - illustration
These are twelve vertebra of the mid back. The last vertebra (on the left side of the picture) attaches to the lumbar (lower) spine, and the top vertebra (on the right) attaches to the cervical (neck) section of the back. The vertebra are broader and stronger than the cervical bones. This allows them to absorb the added pressure applied to the mid back, but they remain a common sight of injury. The vertebra are numbered from one to twelve and labeled T1, T2, T3, et cetera, from the upper most bones to the lowest.
Vertebra, thoracic (mid back)
illustration
-
Vertebral column - illustration
This is the spine and the sacrum with the cervical (neck), thoracic (mid-back), and lumbar (lower back) vertebra. Notice how the appearance of the vertebra change as you look down the spine. The change in shape and size reflect the different functions of the neck, mid-back, and lower back.
Vertebral column
illustration
-
Intervertebral disk - illustration
The vertebral column is made up of 26 bones that provide axial support to the trunk. The vertebral column provides protection to the spinal cord that runs through its central cavity. Between each vertebra is an intervertebral disk. The disks are filled with a gelatinous substance, called the nucleus pulposus, which provides cushioning to the spinal column. The annulus fibrosus is a fibrocartilageous ring that surrounds the nucleus pulposus, which keeps the nucleus pulposus intact when forces are applied to the spinal column. The intervertebral disks allow the vertebral column to be flexible and act as shock absorbers during everyday activities such as walking, running and jumping.
Intervertebral disk
illustration
-
Anterior skeletal anatomy - illustration
The skeleton is made up of 206 bones in the adult and contributes to the form and shape of the body. The skeleton has several important functions for the body. The bones of the skeleton provide support for the soft tissues. For example, the rib cage supports the thoracic wall. Most muscles of the body are attached to bones which act as levers to allow movement of body parts. The bones of the skeleton also serve as a reservoir for minerals, such as calcium and phosphate. Finally, most of the blood cell formation takes places within the marrow of certain bones.
Anterior skeletal anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 8/12/2023
Reviewed By: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.






