Pelvis x-ray
X-ray - pelvisA pelvis x-ray is a picture of the bones in and around both hips. The pelvis connects the legs to the body.
x-ray
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...

How the Test is Performed
The test is done in a radiology department or in the health care provider's office by an x-ray technician.
You will lie down on the table. The pictures are then taken. You may have to move your body to other positions to provide different views.
How to Prepare for the Test
Tell the provider if you are pregnant. Remove all jewelry, especially around your belly and legs. You will wear a hospital gown.
How the Test will Feel
The x-rays are painless. Changing position may cause discomfort.
Why the Test is Performed
The x-ray is used to look for:
-
Fractures
Fractures
If more pressure is put on a bone than it can stand, it will split or break. A break of any size is called a fracture. If the broken bone punctures...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tumors
- Degenerative conditions of bones in the hips, pelvis, and upper legs
- Abnormal shape of your bones or joint
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may suggest:
- Pelvic fractures
-
Arthritis of the hip joint
Arthritis
Arthritis is inflammation or degeneration of one or more joints. A joint is the area where 2 bones meet. There are more than 100 different types of...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Tumors of the bones of the pelvis
Tumors
A bone tumor is an abnormal growth of cells within a bone. A bone tumor may be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sacroiliitis (inflammation of the area where the sacrum joins the ilium bone)
-
Ankylosing spondylitis (abnormal stiffness of the spine and joint)
Ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic form of arthritis. It mostly affects the bones and joints at the base of the spine where it connects with t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Arthritis of the lower spine
- Abnormality of the shape of your pelvis or hip joint
Risks
Children and the fetuses of pregnant women are more sensitive to the radiation of the x-ray. A protective shield may be worn over areas not being scanned or other imaging modalities can be used.
References
Beebe MJ. Fractures of the acetabulum and pelvis. In: Azar FM, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 56.
Kapoor G, Toms AP. Current status of imaging of the musculoskeletal system. In: Adam A, Dixon AK, Gillard JH, Schaefer-Prokop CM, eds. Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology: A Textbook of Medical Imaging. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 38.
Williams KD. Spondylolisthesis. In: Azar FM, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 40.
-
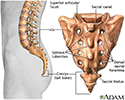
Sacrum - illustration
The sacrum is a shield-shaped bony structure that is located at the base of the lumbar vertebrae and that is connected to the pelvis. The sacrum forms the posterior pelvic wall and strengthens and stabilizes the pelvis. Joined at the very end of the sacrum are two to four tiny, partially fused vertebrae known as the coccyx or tail bone. The coccyx provides slight support for the pelvic organs but actually is a bone of little use.
Sacrum
illustration
-
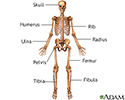
Anterior skeletal anatomy - illustration
The skeleton is made up of 206 bones in the adult and contributes to the form and shape of the body. The skeleton has several important functions for the body. The bones of the skeleton provide support for the soft tissues. For example, the rib cage supports the thoracic wall. Most muscles of the body are attached to bones which act as levers to allow movement of body parts. The bones of the skeleton also serve as a reservoir for minerals, such as calcium and phosphate. Finally, most of the blood cell formation takes places within the marrow of certain bones.
Anterior skeletal anatomy
illustration
-
Sacrum - illustration
The sacrum is a shield-shaped bony structure that is located at the base of the lumbar vertebrae and that is connected to the pelvis. The sacrum forms the posterior pelvic wall and strengthens and stabilizes the pelvis. Joined at the very end of the sacrum are two to four tiny, partially fused vertebrae known as the coccyx or tail bone. The coccyx provides slight support for the pelvic organs but actually is a bone of little use.
Sacrum
illustration
-
Anterior skeletal anatomy - illustration
The skeleton is made up of 206 bones in the adult and contributes to the form and shape of the body. The skeleton has several important functions for the body. The bones of the skeleton provide support for the soft tissues. For example, the rib cage supports the thoracic wall. Most muscles of the body are attached to bones which act as levers to allow movement of body parts. The bones of the skeleton also serve as a reservoir for minerals, such as calcium and phosphate. Finally, most of the blood cell formation takes places within the marrow of certain bones.
Anterior skeletal anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 4/1/2025
Reviewed By: Jason Levy, MD, FSIR, Northside Radiology Associates, Atlanta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.