Skin lesion biopsy
Skin biopsy; Shave biopsy - skin; Punch biopsy - skin; Excisional biopsy - skin; Incisional biopsy - skin; Skin cancer - biopsy; Melanoma - biopsy; Squamous cell cancer - biopsy; Basal cell cancer - biopsyA skin lesion biopsy is when a small amount of skin is removed so it can be examined under a microscope. The skin is tested to look for skin conditions or diseases. A skin biopsy can help your health care provider diagnose or check for problems such as skin cancer or psoriasis.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin condition that causes skin redness, silvery scales, and irritation. Most people with psoriasis have thick, red, well-defined pat...
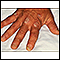
How the Test is Performed
Most procedures can be done in your provider's office or an outpatient medical office. There are several ways to do a skin biopsy. Which procedure you have depends on the location, size, and type of lesion. A lesion is an abnormal area of the skin. This can be a lump, sore, rash, or an area of skin color that is not normal.
Before a biopsy, your provider will numb the area of skin so you don't feel anything. The different types of skin biopsies are described below.
SHAVE BIOPSY
- Your provider uses a small blade or razor to remove or scrape the outermost layers of skin.
- All or part of the lesion is removed.
- You will not need stitches. This procedure will leave a small indented area in your skin.
- This type of biopsy is often done when a skin cancer is suspected, or a rash that seems to be limited to the top layer of skin.
PUNCH BIOPSY
- Your provider uses a cookie cutter-like skin punch tool to remove deeper layers of skin. The area removed is about the shape and size of a pencil eraser.
- If an infection or immune disorder is suspected, your provider may perform more than one biopsy. One of the biopsies is examined under the microscope, the other is sent to the lab for testing such as for germs (skin culture) and certain chemicals.
Skin culture
A skin or nail culture is a laboratory test to look for and identify germs that cause problems with the skin or nails. It is called a mucosal culture...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - It includes all or part of the lesion. You may have stitches to close the area.
- This type of biopsy is often done to diagnose rashes.
Rashes
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
EXCISIONAL BIOPSY
- Your provider uses a surgical knife (scalpel) to remove the entire lesion. This may include deep layers of skin and fat.
- The area is closed with stitches to place the skin back together.
- If a large area is biopsied, your provider may use a skin graft or flap to replace the skin that was removed.
Skin graft or flap
A skin graft is a patch of skin that is removed by surgery from one area of the body and transplanted, or attached, to another area.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - This type of biopsy is most commonly done when a kind of skin cancer called melanoma is suspected.
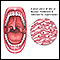
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer. It is also the rarest. It is the leading cause of death from skin disease. Other common types o...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
INCISIONAL BIOPSY
- This procedure takes a piece of a large lesion.
- A piece of the growth is cut and sent to the lab for examination. You may have stitches, if needed.
- After diagnosis, the rest of the growth can be treated.
- This type of biopsy is most commonly done to help diagnose skin ulcers or diseases that involve the tissue below the skin, such as the fatty tissue.
How to Prepare for the Test
Tell your provider:
- About the medicines you are taking, including vitamins and supplements, herbal remedies, drugs, and over-the-counter medicines
- If you have any allergies
Allergies
An allergy is an immune response or reaction to substances that are usually not harmful.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - If you have bleeding problems or take a blood thinner medicine such as aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, warfarin, clopidogrel, dabigatran, apixaban, or other medicines that may inhibit blood clotting
Bleeding
Bleeding disorders are a group of conditions in which there is a problem with the body's blood clotting process. These disorders can lead to heavy a...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - If you are or think you might be pregnant
Follow your provider's instructions on how to prepare for the biopsy.
Why the Test is Performed
Your provider may order a skin biopsy:
- To diagnose the cause of a skin rash
- To see whether a skin growth or skin lesion is a skin cancer
Normal Results
The tissue that was removed is examined under a microscope. Results are most often returned in a few days to a week or more.
If a skin lesion is not a cancer (benign), you may not need any further treatment. If the whole skin lesion was not removed at the time of biopsy, you and your provider may decide to completely remove it.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Once the biopsy confirms the diagnosis, your provider will start a treatment plan. A few of the skin problems that may be diagnosed are:
-
Psoriasis or dermatitis
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin condition that causes skin redness, silvery scales, and irritation. Most people with psoriasis have thick, red, well-defined pat...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection from bacteria or fungus
- Melanoma
-
Basal cell skin cancer
Basal cell skin cancer
Basal cell cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States. Most skin cancers are basal cell cancer. Other common types of skin cancer...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Squamous cell skin cancer
Squamous cell skin cancer
Squamous cell skin cancer is the second most common type of cancer in the United States. Other common types of skin cancer are:Basal cell cancerMelan...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
Risks of a skin biopsy include:
- Infection
- Scar or keloids
Keloids
A keloid is a growth of extra scar tissue. It occurs where the skin has healed after an injury.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
You will bleed slightly during the procedure.
Considerations
You will go home with a bandage over the area. The biopsy area may be tender for a few days afterward. You may have a small amount of bleeding.
Depending on what type of biopsy you had, you will be given instructions on how to care for:
- The skin biopsy area
-
Stitches, if you have them
Stitches
An incision is a cut through the skin made during surgery. It is also called a surgical wound. Some incisions are small. Others are very long. Th...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Skin graft or flap, if you have one
Skin graft or flap
A skin graft is a piece of healthy skin removed from one area of your body to repair damaged or missing skin somewhere else on your body. This skin ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The goal is to keep the area clean and dry. Be careful not to bump or stretch the skin near the area, which can cause bleeding. If you have stitches, they will be taken out in about 3 to 14 days.
If you have moderate bleeding, apply pressure to the area for 10 minutes or so. If the bleeding does not stop, call your provider right away. You should also call your provider if you have signs of infection, such as:
- More redness, swelling, or pain
- Drainage coming from or around the incision that is thick, tan, green, or yellow, or smells bad (pus)
- Fever
Once the wound heals, you may have a scar.
References
Dinulos JGH. Dermatologic surgical procedures. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology: A Color Guide to Diagnosis and Therapy. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 27.
High WA, Tomasini CF, Argenziano G, et al. Basic principles of dermatology. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 0.
Pfenninger JL. Skin biopsy. In: Fowler GC, eds. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 26.
-
Basal Cell Carcinoma - close-up - illustration
This basal cell carcinoma exhibits a characteristic of this type of lesion-telangiectasia. The lesion is also pearly, and smooth, with a slight central depression.
Basal Cell Carcinoma - close-up
illustration
-
Melanoma - neck - illustration
This melanoma on the neck is variously colored with a very darkly pigmented area found centrally. It has irregular borders and appears to be larger than 0.5 cm. Prognosis in melanoma is best defined by its depth on resection.
Melanoma - neck
illustration
-
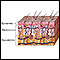
Skin - illustration
The skin is the largest organ of the body. The skin and its derivatives (hair, nails, sweat and oil glands) make up the integumentary system. One of the main functions of the skin is protection. It protects the body from external factors such as bacteria, chemicals, and temperature.
Skin
illustration
-
Basal Cell Carcinoma - close-up - illustration
This basal cell carcinoma exhibits a characteristic of this type of lesion-telangiectasia. The lesion is also pearly, and smooth, with a slight central depression.
Basal Cell Carcinoma - close-up
illustration
-
Melanoma - neck - illustration
This melanoma on the neck is variously colored with a very darkly pigmented area found centrally. It has irregular borders and appears to be larger than 0.5 cm. Prognosis in melanoma is best defined by its depth on resection.
Melanoma - neck
illustration
-
Skin - illustration
The skin is the largest organ of the body. The skin and its derivatives (hair, nails, sweat and oil glands) make up the integumentary system. One of the main functions of the skin is protection. It protects the body from external factors such as bacteria, chemicals, and temperature.
Skin
illustration
Review Date: 8/2/2025
Reviewed By: Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.




