Lung needle biopsy
Transthoracic needle aspiration; Percutaneous needle aspirationA lung needle biopsy is a method to remove a piece of lung tissue for examination. If it is done through the wall of your chest, it is called a transthoracic lung biopsy.
How the Test is Performed
The procedure usually takes 30 to 60 minutes. The biopsy is done in the following way:
- A chest x-ray or chest CT scan may be used to find the exact spot for the biopsy. If the biopsy is done using a CT scan, you may be lying down during the exam.
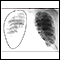
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleChest CT scan
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - You may be given a sedative to relax you.
- You sit with your arms resting forward on a table. Your skin where the biopsy needle is inserted is scrubbed.
- A local painkilling medicine (anesthetic) is injected.
- Your surgeon makes a small cut in your skin.
- The biopsy needle is inserted into the abnormal tissue, tumor, or lung tissue. A small piece of tissue is removed with the needle.
Tumor
A tumor is an abnormal growth of body tissue. Tumors can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - The needle is removed. Pressure is placed on the site. Once bleeding has stopped, a bandage is applied.
- A chest x-ray is taken right after the biopsy.
- The biopsy sample is sent to the lab. Analysis usually takes a few days.
How to Prepare for the Test
You should not eat for 6 to 12 hours before the test. Follow instructions about not taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or blood thinners such as warfarin for a period of time before the procedure. Check with your health care provider before changing or stopping any medicines.
Before a needle biopsy of the lung, a chest x-ray or chest CT scan may be performed.
How the Test will Feel
You will receive an injection of anesthetic before the biopsy. This injection will sting for a moment. You will feel pressure and a brief, sharp pain when the biopsy needle touches the lung.
Why the Test is Performed
A lung needle biopsy is done when there is an abnormal condition near the surface of the lung, in the lung itself, or on the chest wall. Most often, it is done to check for cancer. The biopsy is usually done after abnormalities appear on a chest x-ray or CT scan. Sometimes your provider might recommend a bronchoscopy instead of lung needle biopsy depending on the location of the abnormality.
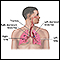
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
Normal Results
In a normal test, the tissues are normal and there is no cancer or growth of bacteria, viruses, or fungi if a culture is performed.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result may be due to any of the following:
- Bacterial, viral, or fungal lung infection
- Cancerous cells (lung cancer, mesothelioma)
Lung cancer
Lung cancer is cancer that starts in the lungs. The lungs are located in the chest. When you breathe, air goes through your nose, down your windpipe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMesothelioma
Malignant mesothelioma is an uncommon cancerous tumor. It mainly affects the lining of the lung and chest cavity (pleura) or lining of the abdomen (...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Benign growth
Risks
Sometimes, a collapsed lung (pneumothorax) occurs after this test. A chest x-ray will be done after the biopsy to check for this. The risk is higher if you have certain lung diseases such as emphysema. Usually, a collapsed lung after a biopsy does not need treatment. But if the pneumothorax is large, there is preexisting lung disease or it does not improve, a chest tube is inserted to expand your lung.
Pneumothorax
A collapsed lung occurs when air escapes from the lung. The air then can fill the space outside of the lung between the lung and chest wall. This b...

Emphysema
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease. Having COPD makes it hard to breathe. There are two main forms of COPD:Chroni...
In rare cases, pneumothorax can be life threatening if air escapes from the lung, gets trapped in the chest, and presses on the rest of your lungs or heart.
Whenever a biopsy is done, there is a risk of too much bleeding (hemorrhage). Some bleeding is common, and a provider will monitor the amount of bleeding. In rare cases, major and life-threatening bleeding can occur.
A needle biopsy should not be performed if other tests show that you have:
- A bleeding disorder of any type
-
Bullae (enlarged alveoli that occur with emphysema)
Bullae
Bullae are large blisters on the skin that are filled with clear fluid. Many different skin conditions can cause bullae to form. They can be caused...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cor pulmonale (condition that causes the right side of the heart to fail)
Cor pulmonale
Cor pulmonale is a condition that causes the right side of the heart to fail. Long-term high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries of the lung an...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cysts of the lung
Cysts
A cyst is a closed pocket or pouch of tissue. It can be filled with air, fluid, pus, or other material.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
High blood pressure in the lung arteries (pulmonary hypertension)
High blood pressure in the lung arterie
Pulmonary hypertension is high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries of the lungs. It makes the right side of the heart work harder than normal....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Severe hypoxia (low oxygen)
Hypoxia
A bluish color to the skin or mucous membrane is usually due to a lack of oxygen in the blood. The medical term is cyanosis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Considerations
Signs of a collapsed lung include:
-
Blueness of the skin
Blueness of the skin
A bluish color to the skin or mucous membrane is usually due to a lack of oxygen in the blood. The medical term is cyanosis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest pain
-
Rapid heart rate (rapid pulse)
Rapid heart rate
A bounding pulse is a strong throbbing felt over one of the arteries in the body. It is due to a forceful heartbeat.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
If any of these occur, call your provider right away.
References
Given MF, Clements W, Thomson KR, Lyon SM. Percutaneous biopsy and drainage of the lung, mediastinum, and pleura. In: Mauro MA, Murphy KPJ, Thomson KR, Venbrux AC, Morgan RA, eds. Image-Guided Interventions. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 103.
Walsh R, Klein JS. Thoracic radiology: invasive diagnostic imaging and image-guided interventions. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 21.
-
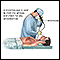
Lung biopsy - illustration
A needle lung biopsy is performed when there is an abnormal condition that is near the surface of the lung, in the tissues surrounding the lungs, or on the chest wall. The test can be performed to obtain a sample for culture when infection of the lung is suspected, and sputum or bronchoalveolar lavage cultures have not identified the cause of the infection.
Lung biopsy
illustration
-
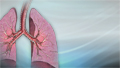
Lung tissue biopsy - illustration
To obtain a sample of lung tissue for biopsy, a needle is inserted within the lung and a sample is withdrawn and sent to the laboratory. The laboratory test isolates and identifies organisms that cause infection from the lung specimen. A lung needle biopsy culture is performed when infection of the lung is suspected and sputum or bronchoalveolar lavage cultures have not identified the cause of the infection.
Lung tissue biopsy
illustration
-
Lung biopsy - illustration
A needle lung biopsy is performed when there is an abnormal condition that is near the surface of the lung, in the tissues surrounding the lungs, or on the chest wall. The test can be performed to obtain a sample for culture when infection of the lung is suspected, and sputum or bronchoalveolar lavage cultures have not identified the cause of the infection.
Lung biopsy
illustration
-
Lung tissue biopsy - illustration
To obtain a sample of lung tissue for biopsy, a needle is inserted within the lung and a sample is withdrawn and sent to the laboratory. The laboratory test isolates and identifies organisms that cause infection from the lung specimen. A lung needle biopsy culture is performed when infection of the lung is suspected and sputum or bronchoalveolar lavage cultures have not identified the cause of the infection.
Lung tissue biopsy
illustration
Review Date: 8/19/2024
Reviewed By: Allen J. Blaivas, DO, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, VA New Jersey Health Care System, Clinical Assistant Professor, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, East Orange, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.



