Intracardiac electrophysiology study (EPS)
Electrophysiology study - intracardiac; EPS - intracardiac; Abnormal heart rhythms - EPS; Bradycardia - EPS; Tachycardia - EPS; Fibrillation - EPS; Arrhythmia - EPS; Heart block - EPSIntracardiac electrophysiology study (EPS) is a test to look at how well the heart's electrical signals are working. It is used to evaluate abnormal heartbeats or heart rhythms.
Heart rhythms
An arrhythmia is a disorder of the heart rate (pulse) or heart rhythm. The heart can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregul...

How the Test is Performed
Wire electrodes are placed in the heart to do this test. These electrodes measure electrical activity in the heart.
The procedure is done in a hospital laboratory. The staff will include a cardiologist (heart doctor), technicians, and nurses.
To have this study:
- Your groin and/or neck area will be cleaned and numbing medicine (anesthetic) will be applied to the skin.
- The cardiologist will then place several IVs (called sheaths) into your groin or neck area. Once these IVs are in place, wires or electrodes can be passed through the sheaths into your body.
- The doctor uses moving x-ray images (fluoroscopy) to guide the catheter into the heart and place the electrodes in the right places.
- The electrodes pick up the heart's electrical signals.
- Electrical signals from the electrodes may be used to make the heart skip beats or produce an abnormal heart rhythm. This can help the doctor understand more about what is causing the abnormal heart rhythm or where in the heart it is starting.
- You may also be given medicines that may also be used for the same purpose.
Other procedures that may also be done during the test:
- Placement of a heart pacemaker
Pacemaker
A pacemaker is a small, battery-operated device. This device senses when your heart is beating too slowly. It sends a signal to your heart that mak...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Procedure to modify small areas in your heart that may be causing your heart rhythm problems (called catheter ablation)
Catheter ablation
Cardiac ablation is a procedure that is used to scar small areas in your heart that may be involved in your heart rhythm problems. This can prevent ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
How to Prepare for the Test
You will be told not to eat or drink for 6 to 8 hours before the test.
You will wear a hospital gown. You must sign a consent form for the procedure.
Your health care provider will tell you ahead of time if you need to make changes to the medicines you regularly take. Do not stop taking or change any medicines without first talking to your provider.
In most cases, you will be given medicine to help you feel calm before the procedure. The test can last from 1 hour up to several hours. You may not be able to drive home afterward, so you should plan for someone to drive you.
How the Test will Feel
You will be awake during the test. You may feel some discomfort when the IV is placed into your arm. You may also feel some pressure at the site when the catheter is inserted. You may feel your heart skipping beats or racing at times.
Why the Test is Performed
Your provider may order this test if you have signs of an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia).
Arrhythmia
An arrhythmia is a disorder of the heart rate (pulse) or heart rhythm. The heart can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregul...

You may need to have other tests before this study is done.
An EPS may be done to:
- Test the function of your heart's electrical system
- Pinpoint a known abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) that is starting in the heart
- Decide the best therapy for an abnormal heart rhythm
- Determine whether you are at risk for future heart events, especially sudden cardiac death
- See if medicine is controlling an abnormal heart rhythm
- See whether you need a pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD)
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
An implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) is a device that detects a life-threatening, rapid heartbeat. This abnormal heartbeat is called an a...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may be due to abnormal heart rhythms that are too slow or too fast. These may include:
-
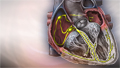
Atrial fibrillation or flutter
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) and atrial flutter are common types of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) which affect the upper chambers (atria) of the...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart block
-
Sick sinus syndrome
Sick sinus syndrome
Normally, the heartbeat starts in an area in the top chambers of the heart (atria). This area is the heart's pacemaker. It is called the sinoatrial...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Supraventricular tachycardia (a group of abnormal heart rhythms that start in the upper chambers of the heart)
Supraventricular tachycardia
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) is episodes of a rapid heart rate that start in a part of the heart above the ventricles. "Paroxysmal...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is a rapid heartbeat that starts in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is a condition in which there is an extra electrical pathway in the heart that leads to periods of rapid heart r...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
There may be other causes that are not on this list.
The provider must find the location and type of heart rhythm problem in order to determine the proper treatment.
Risks
The procedure is very safe in most cases. Possible risks include:
- Arrhythmias
- Bleeding
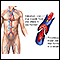
- Blood clots that lead to embolism
Embolism
Blood clots are clumps that occur when blood hardens from a liquid to a solid. A blood clot that forms inside one of your veins or arteries is calle...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cardiac tamponade
Cardiac tamponade
Cardiac tamponade is pressure on the heart that occurs when blood or fluid builds up in the space between the heart muscle and the outer covering sac...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Heart attack
Heart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection
- Injury to the vein
-
Low blood pressure
Low blood pressure
Low blood pressure occurs when blood pressure is below normal. This means the heart, brain, and other parts of the body may not get enough blood. I...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stroke
References
Ferreira SW, Mehdirad AA. The electrophysiology laboratory and electrophysiologic procedures. In: Sorajja P, Lim MJ, Kern MJ, eds. Kern's Cardiac Catheterization Handbook. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 7.
Nattel S, Tomaselli GF. Mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmias. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 62.
Olgin JE. Approach to the patient with suspected arrhythmia. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 49.
-
Cardiac conduction system
Animation
-
Cardiac arrhythmia: Additional tests
Animation
-
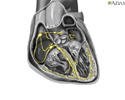
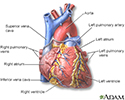
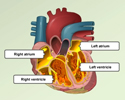
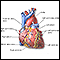
Heart - front view - illustration
The external structures of the heart include the ventricles, atria, arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins carry blood into the heart. The vessels colored blue indicate the transport of blood with relatively low content of oxygen and high content of carbon dioxide. The vessels colored red indicate the transport of blood with relatively high content of oxygen and low content of carbon dioxide.
Heart - front view
illustration
-
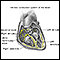
Conduction system of the heart - illustration
The intrinsic conduction system sets the basic rhythm of the beating heart by generating impulses which stimulate the heart to contract.
Conduction system of the heart
illustration
-
Heart - front view - illustration
The external structures of the heart include the ventricles, atria, arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins carry blood into the heart. The vessels colored blue indicate the transport of blood with relatively low content of oxygen and high content of carbon dioxide. The vessels colored red indicate the transport of blood with relatively high content of oxygen and low content of carbon dioxide.
Heart - front view
illustration
-
Conduction system of the heart - illustration
The intrinsic conduction system sets the basic rhythm of the beating heart by generating impulses which stimulate the heart to contract.
Conduction system of the heart
illustration
Review Date: 5/8/2024
Reviewed By: Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.