Ophthalmoscopy
Funduscopy; Funduscopic examOphthalmoscopy is an examination of the back part of the eye (fundus), which includes the retina, optic disc, choroid, and blood vessels.
Retina
The retina is the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eyeball. Images that come through the eye's lens are focused on the retina. Th...
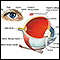
Choroid
The choroid is the layer of blood vessels and connective tissue between the white of the eye and retina (at the back of the eye). It is part of the ...

How the Test is Performed
There are different types of ophthalmoscopy.
- Direct ophthalmoscopy. You will be seated in a darkened room. The health care provider performs this exam by shining a beam of light through the pupil using an instrument called an ophthalmoscope. An ophthalmoscope is about the size of a flashlight. It has a light and different small lenses that allow the provider to view the back of the eyeball.
-
Indirect ophthalmoscopy. You will either lie or sit in a semi-reclined position. The provider holds your eye open while shining a very bright light into the eye using an instrument worn on their head. (The instrument looks like a miner's light.) The provider views the back of the eye through a lens held close to your eye. Some pressure may be applied to the eye using a small, blunt probe. You will be asked to look in various directions. This exam is usually used to look for a detached retina.
Detached retina
Retinal detachment is a separation of the light-sensitive membrane (retina) in the back of the eye from its supporting layers.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Slit-lamp ophthalmoscopy
. You will sit in a chair with the instrument placed in front of you. You will be asked to rest your chin and forehead on a support to keep your head steady. The provider will use the microscope part of the slit lamp and a tiny lens placed close to the front of the eye. The provider can see about the same with this technique as with indirect ophthalmoscopy, but with higher magnification and narrower field of view.
Slit-lamp ophthalmoscopy
The slit-lamp examination looks at structures that are at the front of the eye.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The ophthalmoscopy examination takes about 5 to 10 minutes.
How to Prepare for the Test
Indirect ophthalmoscopy and slit-lamp ophthalmoscopy are often performed after eyedrops are placed to widen (dilate) the pupils. Direct ophthalmoscopy and slit-lamp ophthalmoscopy can be performed with or without the pupil dilated.
You should tell your provider if you:
- Are allergic to any medicines
- Are taking any medicines
- Have glaucoma or a family history of glaucoma
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that can damage the optic nerve. This nerve sends the images you see to your brain. Most often, optic nerve da...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
How the Test will Feel
The bright light will be uncomfortable, but the test is not painful.
You may briefly see images after the light shines in your eyes. The light is brighter with indirect ophthalmoscopy, so the sensation of seeing after-images may be greater.
Pressure on the eye during indirect ophthalmoscopy may be slightly uncomfortable, but it should not be painful.
If eyedrops are used, they may sting briefly when placed in the eyes. You may also have an unusual taste in your mouth.
Why the Test is Performed
Ophthalmoscopy may be done as part of a routine physical but is always part of a complete eye examination.
It is used to detect and evaluate symptoms of retinal detachment or eye diseases such as glaucoma.
Ophthalmoscopy may also be done if you have signs or symptoms of high blood pressure, diabetes, or other diseases that affect the blood vessels.
Normal Results
The retina, blood vessels, and the optic disc appear normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may be seen on ophthalmoscopy with any of the following conditions:
- Viral inflammation of the retina (CMV retinitis)
CMV retinitis
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis is a viral infection of the retina of the eye resulting in inflammation.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Diabetes
Diabetes
Diabetes can harm the eyes. It can damage the small blood vessels in the retina, the back part of your eye. This condition is called diabetic retin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Glaucoma
- High blood pressure
- Loss of sharp, central vision due to age-related macular degeneration
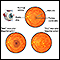
Age-related macular degeneration
Macular degeneration is an eye disorder that slowly destroys sharp, central vision. This makes it difficult to see fine details and read. The diseas...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Melanoma of the eye
Melanoma of the eye
Melanoma of the eye is cancer that occurs in various parts of the eye.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Optic nerve problems
- Separation of the retina in the back of the eye from its supporting layers (retinal detachment)
Ophthalmoscopy is considered to be 90% to 95% accurate. It can detect the early stages and effects of many serious diseases. For conditions that cannot be detected by ophthalmoscopy, there are other techniques and devices that may be helpful.
Risks
If you receive drops to dilate your eyes for the ophthalmoscopy, your vision will be blurred.
- Wear sunglasses to protect your eyes from sunlight, which can damage your eyes.
- Have someone drive you home.
- The drops usually wear off in several hours.
The test itself involves no risk. In rare cases, the dilating eyedrops cause:
- An attack of narrow-angle glaucoma
-
Dizziness
Dizziness
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Dryness of the mouth
- Flushing
-
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
If narrow-angle glaucoma is suspected, dilating drops are usually not used.
References
Atebara NH, Miller D, Thall EH, Brodie SE. Ophthalmic instruments. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 2.5.
Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW. Eyes. In: Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW, eds. Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination. 10th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 12.
Chuck RS, Dunn SP, Flaxel CJ; American Academy of Ophthalmology Preferred Practice Pattern Committee, et al. Comprehensive adult medical eye evaluation preferred practice pattern. Ophthalmology. 2021;128(1):P1-P29. PMID: 34933742 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34933742/.
-
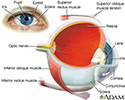
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer (sclera, or white of the eye, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (retina) is sensory nerve tissue that is light sensitive. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
-
Internal eye anatomy - illustration
The cornea is the clear watch glass covering in the front of the eye. The cornea works with the lens of the eye to focus images on the retina. The retina is the internal layer of the eye that receives and transmits focused images. The retina is normally red due to its rich blood supply.
Internal eye anatomy
illustration
-
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer (sclera, or white of the eye, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (retina) is sensory nerve tissue that is light sensitive. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
-
Internal eye anatomy - illustration
The cornea is the clear watch glass covering in the front of the eye. The cornea works with the lens of the eye to focus images on the retina. The retina is the internal layer of the eye that receives and transmits focused images. The retina is normally red due to its rich blood supply.
Internal eye anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 1/20/2025
Reviewed By: Franklin W. Lusby, MD, Ophthalmologist, Lusby Vision Institute, La Jolla, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.