Low blood pressure
Hypotension; Blood pressure - low; Postprandial hypotension; Orthostatic hypotension; Neurally mediated hypotension; NMHLow blood pressure occurs when blood pressure is below normal. This means the heart, brain, and other parts of the body may not get enough blood. In adults, the normal blood pressure is between 90/60 mmHg and 120/80 mmHg.
The medical word for low blood pressure is hypotension.
Causes
Blood pressure varies from one person to another and also over time for any given person. A drop of as little as 20 mmHg can cause problems for some people. There are different types and causes of low blood pressure.
Severe hypotension (shock) can be caused by sudden loss of blood (shock), severe infection, heart attack, or severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis).
Shock
Shock is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body is not getting enough blood flow. Lack of blood flow means the cells and organs do n...

Heart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening type of allergic reaction.

Orthostatic hypotension means your blood pressure drops when you shift from lying down to standing. This type of low blood pressure usually lasts only a few seconds or minutes. If this type of low blood pressure occurs after eating, it is called postprandial orthostatic hypotension. This type most often affects older adults, those with high blood pressure, and people with Parkinson disease.
Parkinson disease
Parkinson disease results from certain brain cells dying. These cells help control movement and coordination. The disease leads to shaking (tremors...
Neurally mediated hypotension (NMH) most often affects young adults and children. It can occur when a person has been standing for a long time. Children usually outgrow this type of hypotension.
Certain medicines and substances can lead to low blood pressure, including:
- Alcohol
- Anti-anxiety medicines
- Certain antidepressants
- Diuretics
- Heart medicines, including those used to treat high blood pressure and coronary heart disease
High blood pressure
Blood pressure is a measurement of the force exerted against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood to your body. Hypertension is the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCoronary heart disease
Coronary heart disease is a narrowing of the blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart. Coronary heart disease (CHD) is also called co...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines used for surgery
- Painkillers
Other causes of low blood pressure include:
-
Nerve damage from diabetes or other disorders
Nerve damage from diabetes
Nerve damage that occurs in people with diabetes is called diabetic neuropathy. This condition is a complication of diabetes.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Changes in heart rhythm (arrhythmias)
Arrhythmias
An arrhythmia is a disorder of the heart rate (pulse) or heart rhythm. The heart can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregul...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Not drinking enough fluids (dehydration)
Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when your body does not have as much water and fluids as it needs. Dehydration can be mild, moderate, or severe, based on how much...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Symptoms of low blood pressure may include:
- Blurry vision
-
Confusion
Confusion
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Dizziness
Dizziness
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fainting (syncope)
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Lightheadedness
-
Nausea or vomiting
Nausea or vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sleepiness
-
Weakness
Weakness
Weakness is reduced strength in one or more muscles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you to determine the cause of your low blood pressure. Your vital signs (temperature, pulse, rate of breathing, and blood pressure) will be checked frequently. You may need to stay in the hospital for a while.
Your provider will ask questions, including:
- What is your normal blood pressure?
- What medicines do you take?
- Have you been eating and drinking normally?
- Have you had any recent illness, accident, or injury?
- What other symptoms do you have?
- Did you faint or become less alert?
- Do you feel dizzy or lightheaded when standing or sitting after lying down?
The following tests may be done:
-
Basic metabolic panel
Basic metabolic pane
The basic metabolic panel is a group of blood tests that provides information about your body's metabolism.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blood cultures to check for infection
Blood cultures
A blood culture is a laboratory test to check for bacteria or other germs in a blood sample.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Complete blood count (CBC), including white blood cell differential
CBC
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
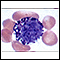
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleWhite blood cell differential
The blood differential test measures the percentage of each type of white blood cell (WBC) that you have in your blood. It also reveals if there are...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
X-ray of the abdomen
X-ray of the abdomen
An abdominal x-ray is an imaging test to look at organs and structures in the abdomen. Organs include the liver, spleen, stomach, and intestines. T...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
X-ray of the chest
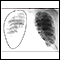
X-ray of the chest
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Lower than normal blood pressure in a healthy person that does not cause any symptoms often does not need treatment. Otherwise, treatment depends on the cause of your low blood pressure and your symptoms.
When you have symptoms from low blood pressure, sit or lie down right away. Then raise your feet above heart level.
Severe hypotension caused by shock is a medical emergency. You may be given:
- Blood or other fluids through a needle (IV)
IV
Intravenous means "within a vein. " Most often it refers to giving medicines or fluids through a needle or tube inserted into a vein. This allows th...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines to increase blood pressure and improve heart strength
- Other medicines, such as antibiotics
Treatments for low blood pressure after standing up too quickly include:
- If medicines are the cause, your provider may change the dosage or switch you to a different medicine. Do not stop taking any medicines before talking to your provider.
- Your provider may suggest drinking more fluids to treat dehydration.
- Wearing compression stockings can help keep blood from collecting in the legs. This keeps more blood in the upper body.
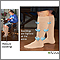
Compression stockings
You wear compression stockings to improve blood flow in the veins of your legs. Compression stockings gently squeeze your legs to move blood up your...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
People with NMH should avoid triggers, such as standing for a long period of time. Other treatments include drinking fluids and increasing salt in your diet. Talk to your provider before trying these measures. In severe cases, medicines may be prescribed.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Low blood pressure can usually be treated with success.
Possible Complications
Falls due to low blood pressure in older adults can lead to a broken hip or spine fracture. These injuries can reduce a person's health and ability to move about.
Sudden severe drops in your blood pressure starve your body of oxygen. This can lead to damage of the heart, brain, and other organs. This type of low blood pressure can be life threatening if not treated right away.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If low blood pressure causes a person to pass out (become unconscious), seek treatment right away. Or call 911 or the local emergency number. If the person is not breathing or has no pulse, begin CPR.
CPR
CPR stands for cardiopulmonary resuscitation. It is an emergency life-saving procedure that is done when someone's breathing or heartbeat has stoppe...
Call your provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- Black or maroon stools
-
Chest pain
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Dizziness, lightheadedness
- Fainting
- Fever higher than 101°F (38.3°C)
-
Irregular heartbeat
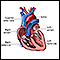
Irregular heartbeat
Palpitations are feelings or sensations that your heart is pounding or racing. They can be felt in your chest, throat, or neck. You may:Have an unpl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Prevention
Your provider may recommend certain steps to prevent or reduce your symptoms including:
- Drinking more fluids
- Getting up slowly after sitting or lying down
- Not drinking alcohol
- Not standing for a long time (if you have NMH)
- Using compression stockings so blood does not collect in the legs
References
Calkins H, Everett TH, Chen P-S. Hypotension and syncope. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 71.
Schrigern DL. Approach to the patient with abnormal vital signs. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 7.
Review Date: 1/1/2025
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor Emeritus, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


